Select Road Overlay
The third and final step is to identify the road dataset to associate with AVLS and how the data from this run should be loaded into the Speed database.
Select Applications > AVLS > Load AVLS Data.
This opens the overlay selection dialog.
1. Road overlay
Click the … button to open a SIS 9 overlay browser and select your overlay.
TIP: The AVLS add-in may be hidden when the overlay browser is open.
An overlay containing OS Highways, OS OpenRoads or OS ITN as created by the Network Manager or OpenData Loader must be selected. The add-in checks the dataset’s feature table so it can determine what road link attribute to use.
If any other overlay is selected you may see an error message: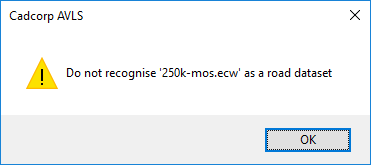
2. Snap Radius
Specify a snap radius – this is used in the matching of an AVLS point to a link. If there is no link within the snap radius, the AVLS point will be discarded (useful for when journeys are not in an area covered by the Road network).
If there is more than one link within the snap radius, the nearest is used.
Note: See ‘Use bearing’ below.
3. Mode
The Load can be run in one of two modes:
- Add to existing… - all AVLS data points accepted are added to the existing set.
- Replace existing… - if there are already records in the Speed database matching the road link identifier, these existing records will be deleted.
4. Ignore speeds
The Add-In can ignore AVLS speeds below a specified value or above a specified value. This is useful to remove gross errors in the data.
Leave these fields blank if you do not want to specify any limits.
5. Use bearing
This uses a bearing in the AVLS point record in the selection of the nearest link.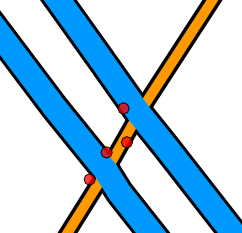
The picture above shows AVLS data points (red circles) where a B road crosses a motorway.
If these are snapped to the nearest link, it is possible that points which belong to the B road might be attributed to the motorway and vice-versa.
If ‘Use bearing’ is enabled, the bearing at the point is compared with the bearing of the link at that point.
The point is now associated with that link (provided it falls within the tolerance specified in degrees on the form - e.g., 20° in the example above)
In the above image, note the top-most AVLS point has a bearing of 142° which means its speed (53MPH) becomes associated with the motorway. The AVLS point immediately below it has a bearing of 211° which means its speed (44MPH) is associated with the B road.
Note: This option will be greyed out if the AVLS data files do not contain bearing information.
6. Create an overlay
This causes an internal overlay to be created containing the AVLS data points added to the database during this load.
On clicking Next
If the AVLS data is being loaded from SQL Server, the next page will be Load AVLS Data- §3.4.
If the AVLS data is being loaded from data files and the configured format contains status values, you will see Status Values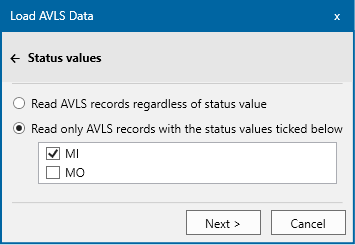
The Load page will follow the Status Values.
If points in the AVLS data file(s) contain an unlisted status, these points are ignored.
Note: You will be advised of all unknown statuses at the end of the load.
