Geographic Unit
You can select any geographic unit to use for risk modelling. Examples of geographic units include station grounds, wards, output areas or grids.
If you require a grid, use the Grid command below to create an overlay containing area items. These items are usually set out to define a regular grid.
Each grid cell is formed of an area item with a Row& and Column& attribute of its position in the grid. The resultant grid overlay is suitable for use as Geographic Units in a Risk command.
Note: The Grid command is intended for use only with a rectangular co-ordinate system.
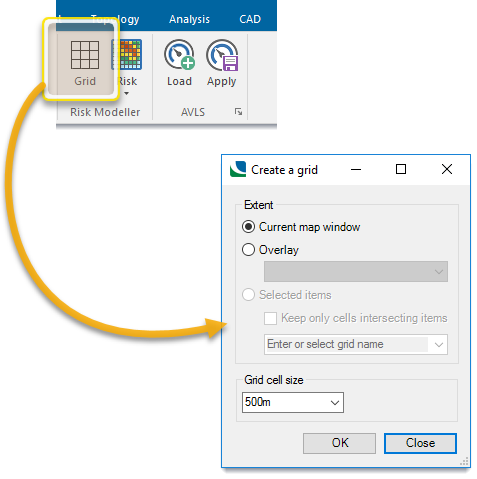
Click Applications > Risk Modeller > Grid to open the grid options:
Extent
Specify the grid extent- it can be the current map window, a specified overlay or any selected item.
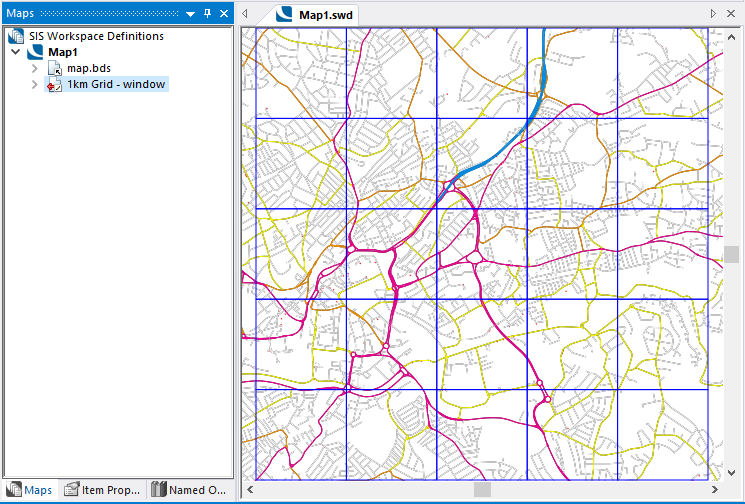
Use this option to create a grid just big enough to cover the current map window.
You will be shown the number of cells that will be created. 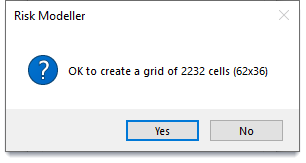
Click Yes to create a new overlay containing the grid.
The new overlay will take the name of the grid size (in this case 1km) followed by the extent selected (in this case window)
Select this option to create a grid just big enough to cover the extent of all the items in a selected overlay. (Invisible overlays are not included in the drop-down list.)
You will be shown the number of cells that will be created.
Click Yes to create a new overlay containing the grid.
The new overlay will take the name of the grid size (in this case 1km) followed by the extent selected (in this case overlay name)
Select this option to create a grid to cover the extent of the selected items.
Note: If multiple items are selected, the grid will also cover the space between the items.
Keep only cells intersecting items: Enable this option to remove grid cells covering just ‘space’ (i.e. the resultant grid will cover only the selected items.)
You will be shown the number of cells that will be created (this number always refers to the initial grid, i.e. including space between the selected items.)
Click Yes to create a new overlay containing the grid.
The new overlay will take the name of the grid size either Selected item(s) or the text entered in the box Enter or select grid name.)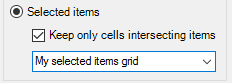
The drop-down includes the values of string ($) attributes of the first item selected.
Changing the default entry as shown above will give the overlay the name: 1km Grid - My selected items grid
This example shows the default overlay name, Selected item(s), if the drop-down box is not changed: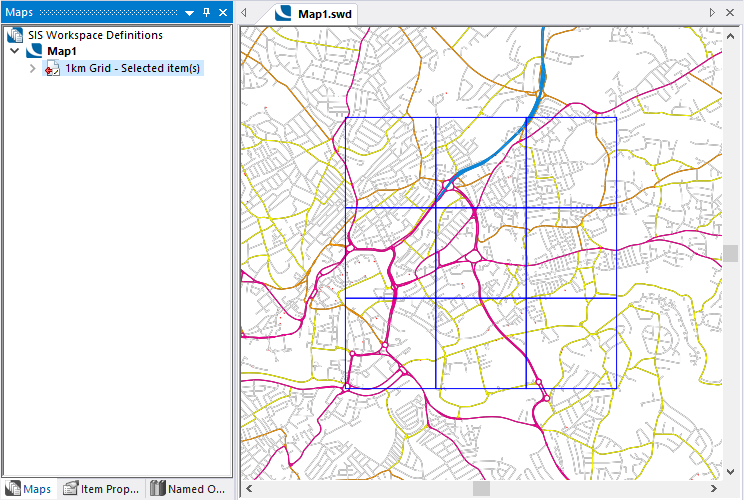
Grid cell size
Use these options to specify the grid cell size.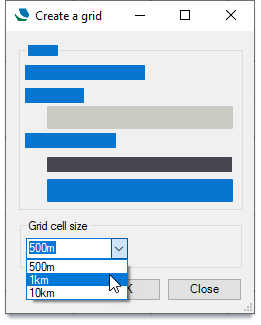
You can also enter your own grid size (for e.g.2km)
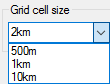
Each of these sizes creates a grid where the grid cells have an attribute containing their OS reference (if they are within the overall bounds on the OS GB system)
For example:
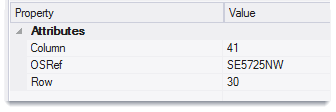
For any user-defined cell size (i.e. sizes other than 500m, 1km or 10km) each cell in the created grid will have an X,Y tile reference but no OS tile reference.
Other sizes can be used in the box for grid cell but must conform to the following rules:
- A single number defines the size of a square cell
- Two numbers separated by an x define the width and height of a rectangular cell
- Numbers cannot be decimals
- Units can be either m or km (metres of kilometres)
- If no units are specified, the number will be treated as metres.
- If two numbers are entered but only one has a unit then both are regarded as being in that unit.
Examples of user-defined cell sizes:
|
50 |
= 50m x 50m cell size |
|
75m |
= 75m x 75m cell size |
|
1x2km |
= 1000m x 2000m cell size |
|
500m x 1km |
= 500m x 1000m cell size |