Microsoft SQL Server Spatial
![]()
Select Home > Add Overlay > Databases > Microsoft SQL Server Spatial and click Next.
Before accessing spatial data from a SQL Server database, ensure the SIS Map Window is focused in the correct location and at a reasonable scale for the data being accessed (i.e 1:1250).
SIS Desktop will automatically select data from the database that coincides with the map extents of the map window.
Note: The Microsoft SQL Server Spatial requires SQL Server 2008 or later because it relies on the spatial datatype.
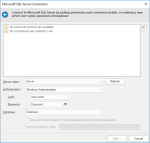
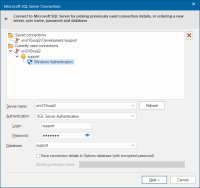
Enter your connection details for SQL Server or select a previously saved connection.
| Option | Description | |
|
Server name |
Select a server name from the drop-down list or type the name of the SQL Server instance. Selecting the database on the server is a separate action. Click Refresh to refresh the list. If the server instance uses a port other than the default, specify the port after the server address like this: Server\SQL2016, 1434 |
|
|
Authentication |
Windows Authentication: If SQL Server has been set up to use Windows Authentication, select this option. The SQL Server system administrator must have associated your Microsoft Windows network ID with a SQL Server login ID. SQL Server Authentication: Select to use a supplied user name and password to authenticate your logon information to the data source. |
|
|
Login |
Type the user ID for SQL Server Login |
|
|
Password |
Type the password to use for authentication when you log on to the data source. |
|
|
Database |
Type the name of the SQL Server database you want to access or select it from the drop-down box. |
|
|
Save connection details in UI settings database (with encrypted password) |
Check this tickbox to store database connection details for future use. The password will be stored in encrypted form for security. |
|
|
Saved connection name |
Enter a meaningful name to save this connection. Previously used names cannot be used. |
|
If the Microsoft SQL Server Connection has been made previously and the connection details saved, they are now displayed.
In this case click on one of the Saved connections or Currently used connections (if any are in use) to complete the connection details. Click Next.
The Database connection type dialog will be displayed:
- Select Simple to see a list of one or more spatial database tables with default configuration options.
- Check the tickboxes for the SQL Server tables you want to open in SIS Desktop as overlays.
- Adjust the ‘The Coordinate Reference System’ if necessary. For most users, the default value can be retained.
- Click Finish.
- This option opens a single database table with options to configure the connection type made to the database & an optional feature table.
- Select the table from the list in the Microsoft SQL Server Spatial Data Sources window.
- Adjust the ‘The Coordinate Reference System’ if necessary. For most users, the default value can be retained.
- Click Next.
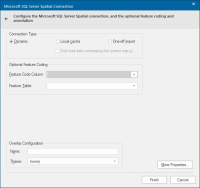
- The Microsoft SQL Server Spatial Connection dialog will be displayed to enable the connection to be configured:
Connection Type
1. Dynamic
This is the default connection type and is only available if the table has a spatial index present. This option allows editing if the correct permissions are present on the database.
The Dynamic connection type maintains an open/active connection to the database throughout the SIS session. A redraw in the map window causes SIS Desktop to request fresh data from the SQL Server Database based on the current view extents.
This becomes very important in a multi-user environment as edits made to the data by other users are displayed after the map has been refreshed.
Note: Dynamic connection requires spatial index on the table and column.
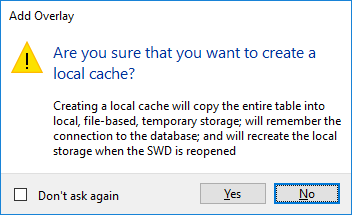
2. Local cache
This connection type creates an overlay that is a local copy of the entire table or the area that overlaps the current view extent.
The connection to the database does not remain open; as a result refreshes in the map window do not return data from the database. Data in the overlay remains in the client memory for the duration of the session.
The overlay is created as a read only dataset. If you save the SWD when it is open, SIS Desktop will read the data from the database and place the new data into memory.
Opening tables containing a large amount of data (100,000 features or more) may affect client performance depending on the amount of RAM available.
Click Yes to create a local cache and load the entire table into local file-based temporary storage.
3. One-off import
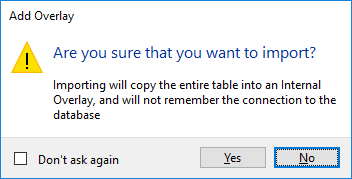
This connection type creates an overlay that is a replica of the entire table (or the area that overlaps the current view extent if appropriate check box is ticked.)
The connection to the database does not remain open. As a result, refreshes in the map window do not return data from the database. Data in the overlay remains as a copy in an internal overlay as a part of the SWD file.
The overlay is created as an editable dataset. If you save the SWD when it is open, SIS Desktop will NOT read the data from the database.
Opening tables containing a large amount of data (100,000 features or more) may affect client performance depending on the amount of RAM available.
Click Yes to import the table into an internal overlay.
Note: SIS Desktop does not remember the Connection Type settings between uses of a database connection and will always default to Dynamic.
4. Only load data overlapping the current map view extents: Available for Local cache and One-off import connection types only.
Optional Feature Coding
If you intend to use a feature table with your overlay, ensure the Microsoft SQL Server table contains the appropriate feature code attribute as well as the geometry type containing the spatial data.
If your data was loaded using the Cadcorp OS MasterMap Manager, the feature code is automatically exported for you. If you created your dataset using the export utility in SIS Desktop, ensure the feature code column is listed in the overlay schema before exporting the overlay.
Alternatively if there is no feature code attribute you can generate one manually using one of the Microsoft SQL Server database interfaces such as SQL Plus.
To apply a feature table select the feature code attribute from the drop-down list. The feature code attribute must be in the Microsoft SQL Server table in a column of a number type.
Select the appropriate feature table from the Feature Table drop-down list.
Overlay Configuration
Name: Specify a name for the overlay. If no name is supplied, a default name will be assigned (this name will include the database connection information and table.)
Theme: Specify a theme to associate with the data. (optional)
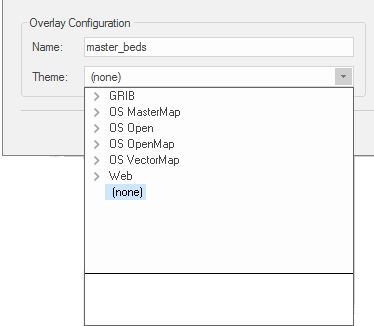
To make changes click More Properties. If you do not want to modify the dataset's Coordinate Reference System, scale, etc. click Finish. The ASQLServerCursorDTS dialog will be displayed:
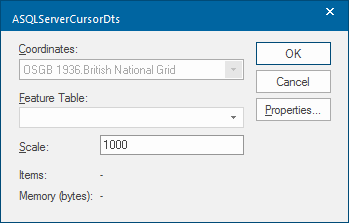
Coordinates: Displays the coordinate reference system the dataset items are defined in.
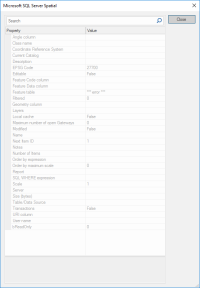
Scale: The default viewing scale for this dataset. This will affect how Text items convert their point heights into world sizes. Click the Properties... button to display the resizeable Microsoft SQL Server Spatial Dataset dialog:
This dialog enables columns from the Microsoft SQL Server spatial table to be mapped to SIS properties which in the case of Angle column (_angleColumn$) allows symbols to be rotated by the angle specified for that row in the table.
For example if your symbol rotation value is stored in COLUMN_X, enter COLUMN_X.
In the case of the URI column (_uriColumn$) the Open Link command can be used to link to a given feature by entering the name of the PostGIS table column that contains the data. The column name must "exactly" match the case of the column in the database.
For example if you have a series of photographs stored in COLUMN_X, enter COLUMN_X.
Click Close in the Microsoft SQL Server Spatial Datasetost dialog and click OK in the ASQLServerCursorDTS dialog to return to the Microsoft SQL Server Spatial Connection dialog and click Finish.
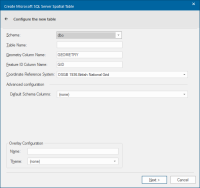
The Create Microsoft SQL Server Spatial Table dialog will be displayed.
This option creates an new empty dataset (ie a new table in SQL Serve)
|
Option |
Description |
|
|
Schema |
Select the schema from the drop-down list. |
|
|
Table Name |
The name of the SQL Server spatial layer. You can enter any SQL server compliant table name. |
|
|
Geometry Column Name |
The name for the column in the SQL Server table is GEOMETRY, and is type geometry. The name of the column can be changed. |
|
|
Feature ID column |
The name of the Feature ID column- – this will become the primary key for the table in the database. |
|
|
Coordinate Reference System |
The Coordinate Reference System associated with the spatial layer defaults to the Coordinate Reference System for the overlay. |
|
|
Default Schema Columns |
Use the drop-down to select the required default schema column: |
|
|
Overlay Configuration |
Name: This is the full name of the selected overlay which can be edited. Theme: This drop-down shows any Themes associated with the overlay:
|
|
When you choose a theme from the drop-down and click Next, the Cursor Dataset Details dialog opens. Configure the dataset as necessary:
Specify the necessary information to create a new table in SQL Server
Note: After the table in created in SQL Server an overlay (based on the same table) is added to the current session ready for you to add data.
|
Option |
Description |
|
|
Column |
Attribute information can be stored in a column. Add as many columns as you require. Specify the appropriate datatype for your new column. |
|
|
Index |
Optionally add an index to the column in SQL Server. Note: Indexes should be added to columns that will be used for filtering data. |
|
|
Feature Table and Feature Code Column |
Optionally apply a feature table to the overlay |
|
|
Feature Data Column |
Optionally specify a Feature Data Column |
|
|
Dimension |
Optionally specify ‘XYZ if the table will be used to store height information |
|
|
Version |
Specify the OGC Simple Features version to be used by the overlay |
|
|
Transactions |
Check this box to ensure edits to the resulting overlay can only be made within a transaction. |
|
Transactions
Transactions are a database concept. A transaction allows users to make a series of edits to data without making permanent changes in the database.
During a transaction the current user is the only user that sees the changes being made. Other users see the data as it was prior to the changes being made.
The active user can then choose to make the changes permanent by committing the changes or undoing the changes by rolling back the data.
Click on Begin to start a transaction. Begin editing the data.
After the edits are completed either ‘Commit’ or ‘Rollback’ the changes.
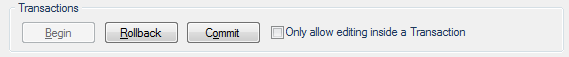
Rollback
This will release the transaction and allow other users to obtain editable access to the data. The changes you made are not applied to the dataset.
Note: Regenerating an overlay whilst in the middle of a transaction causes the transaction to rollback. In addition all undo information for the overlay will be cleared.
Commit
This will commit the changes permanently to the database and release the transaction. All users will now be able to view the data.
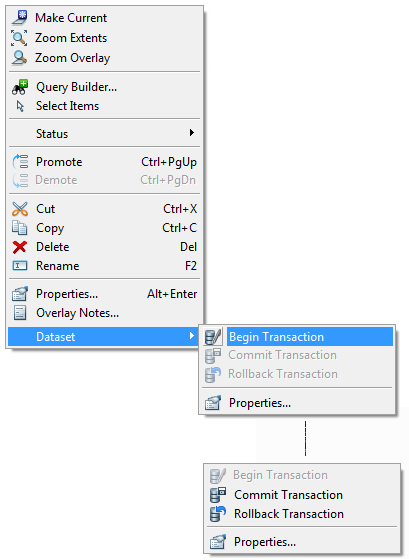
Alternatively the three Transaction commands; Begin, Commit and Rollback may also be accessed locally as shown below:
Only allow editing inside a Transaction
Check this tickbox to ensure no edits can be made outside of the current transaction.
-none selected_thumb_200_0.png)
_thumb_200_0.png)