Isochrones
Isochrones show not just the physical distance between places but the time it takes to get from one spot to another.
Select Analysis > Routing > Isochrones.
This opens the Isochrones dialog: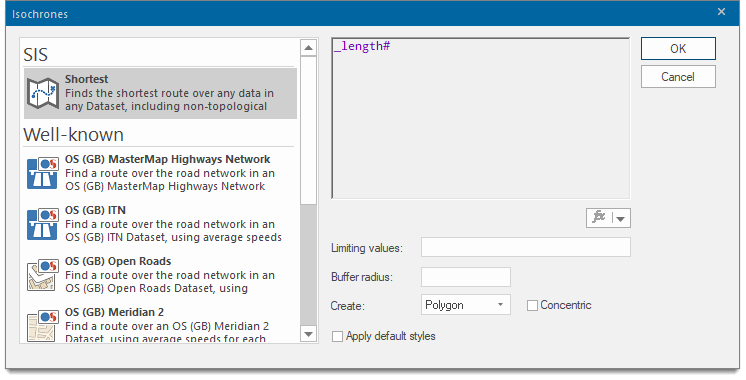
Select one of the options.
- Shortest - Show all locations that can be reached via a route shorter than the distance entered as a Limiting value
- Well-known- choice of well-known mapping networks.
- Custom Expression - Select this option to use an expression to calculate the isochrone. For example, an expression may be used to take into account the speed limits on the roads in order to calculate an isochrone based on time rather than distance.
Well-known Route options
Finds the cheapest route using a well-known expression as the 'cost' of a link. Many of these options are similar to the ones available in other routing options.
- HERE Map
- OS (GB) MasterMap Highways Network
- OS (GB) NGD Transport Network
- OS (GB) Open Roads
Custom Expression
You can also use the SQL Control Bar from the View ribbon tab to create routes. For instance to create a route from each Fire Station to each Incident that the Station responded to, you can create a SQL statement as follows.
.create stationIncidents
Select st_findroute(Incidents.sis_geometry,Stations.sis_geometry,
'{"OSRM":{"File":"British Isles.osrm"}}')
from Incidents join Stations on Incidents.Station_Name = Stations.Station_Name;Creating an isochrone (Example):
- Select Analysis > Routing > Isochrones.
- Scroll down the list to select OS (GB) Open roads.
- In the Limiting value edit text box, type the value 2 (this is a route cost of 2 mins)
- Set the Buffer radius to 50. This number denotes how large a buffer is drawn around the routes. Set to 0 if you do not need a buffer.
- From the Create dropdown, select QZone.
- Tick the Apply default styles tickbox.
- Click OK.
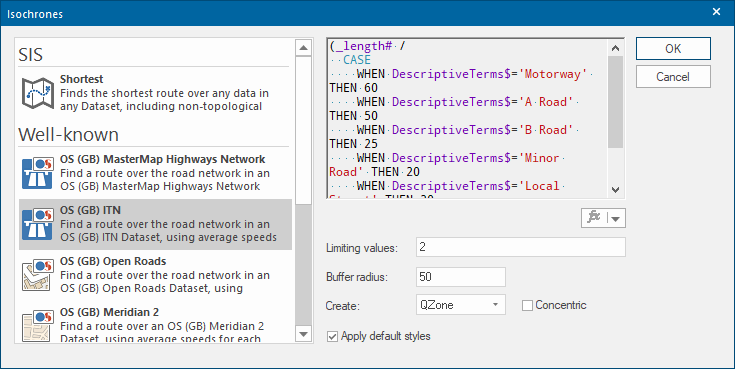
- Click on the map at your chosen start position.
-
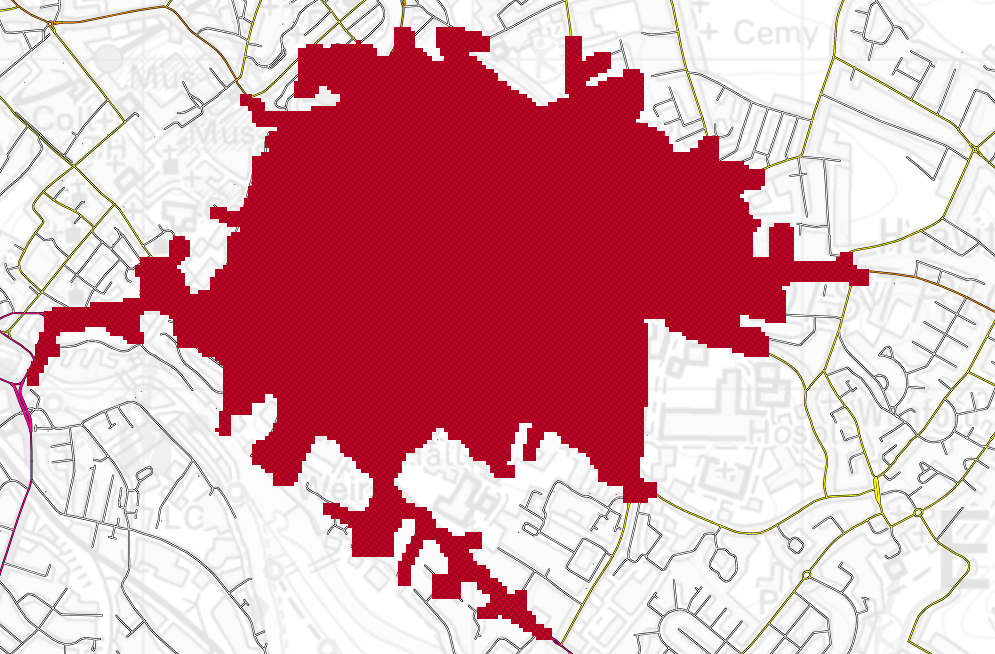
The Isochrone is created
as below.
Iso-chrones from items
Creates isochrones on a network from the origin(s) of a selected item(s).
An isochrone is created from the origin of each point, showing how far you can travel from that point using the network. For e.g. to visually determine the area you can cover using vehicles at selected locations using a relevant travel time.