Operators
Arithmetic
Examples:
6-10
returns -4
maximumValue# - minimumValue#
returns the difference between maximumValue# and minimumValue#
Examples:
5.678 % 1.234
returns 0.742
_area# % _sx#
returns the remainder from the division of _area# by _sx#
Example:
1.234 * 5.678
returns 7.006652
_area# * _sx#
returns the result of _area# multiplied by _sx#
Example:
1.234/5.678
returns 0.217330045790771
_area#/_length#'
returns the result of _area# divided by _length#
Examples:
1.234^5
returns 2.86138172105142
_length#^2
returns _length# to the power of 2
Examples:
1.234 + 5.678returns 6.912
_ox# + sx#
returns the sum of _area# and _sx#
Comparison
Examples:
valueA#<1.234
returns -1 if valueA# is less than 1.234, returns 0 if valueA# is not less than 1.234 (or if valueA# is equal to 1.234).
valueA#<valueB#
returns -1 if valueA# is less than valueB#, returns 0 if valueA# is not less than valueB# (or if valueA# is equal to valueB#).
Examples:
valueA#<=100
returns -1 if valueA# is less than or equal to 100, returns 0 if valueA# is not less than or equal to 100.
valueA#<=valueB#
returns -1 if valueA# is less than or equal to valueB#, returns 0 if valueA# is not less than or equal to valueB#.
Examples:
valueA#<>1.234
returns -1 if valueA# is different to 1.234, returns 0 if valueA# is not different to 1.234.
valueA#<>valueB#
returns -1 if valueA# is different to valueB#, returns 0 if valueA# is not different to valueB#.
Examples:
valueA#=1.234
returns -1 if valueA# is equal to 1.234, returns 0 if valueA# is not equal to 1.234.
valueA#=valueB#
returns -1 if valueA# is equal to valueB#, returns 0 if valueA# is not equal to valueB#.
Examples:
valueA#>1.234returns -1 if valueA# is greater than 1.234, returns 0 if valueA# is not greater than 1.234.
valueA#>valueB#returns -1 if valueA# is greater than valueB#, returns 0 if valueA# is not greater than valueB#.
Examples:
valueA#>=1.234
returns -1 if valueA# is greater than or equal to 1.234, returns 0 if valueA# is not greater than or equal to 1.234.
valueA#>=valueB#
returns -1 if valueA# is greater than or equal to valueB#, returns 0 if valueA# is not greater than or equal to valueB#.
Expression Syntax: number Between low And high
number
a number or property to be taken to see if it is between low and high.
low
the lower limit of the range. Can be a number or a property.
high
the higher limit of the range. Can be a number or a property.
Examples:
value# Between 0 And maximumValue#
returns -1 if value# is between 0 and maximumValue#, returns 0 if value# is not between 0 and maximumValue#.
valueA# Between valueB# And valueC#
returns -1 if valueA# is between valueB# and valueC#, returns 0 if valueA# is not between valueB# and valueC#.
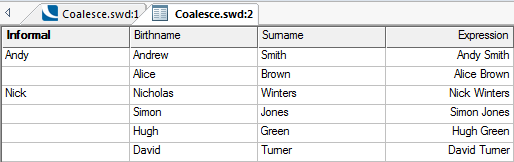
Coalesce functions in a manner similar to a concatenate command. When stringing two columns together a nil return will occur if there is no value in every single column.
Coalesce prevents this possibility by using a value if it exists but taking a value from another column if it doesn't.
Example:
The following code tells Coalesce to use Informal name if it exists but if it does not exist then use Birthname.
Coalesce(Informal$, Birthname$)
Note: Not every entry has (or needs) to have an Informal name.
Can be used to test for similar text strings.
Example:
Fuzzy("This is my sample text for testing results",Text$)If the text in quotes and the text in Text$ are identical then 1 will be returned, indicating they are identical.
If the two texts differ slightly then a figure of less than 1 will be returned. The more the two texts differ the lower the returned value will be. If the texts bear no similarity at all a value of 0 will be returned.
Can be used to test for identical text strings between strings and properties.
Expression Syntax: Grep(regexp, string)
regexp
The regular expression to be searched for.
string
The text string or property to be searched.
Examples:
Grep("Customi[sz]e", _text$)
Matches any of the enclosed characters, i.e. 's' or 'z'.
will return -1 for Customise or Customize
Grep("Customi[^sz]e", _text$)
Matches anything NOT enclosed by the brackets
will return -1 for Customixe, if such a word was found, will return 0 for any other text strings.
Further examples;
i(?=z)Matches 'i' only if 'i' is followed by 'z'.
x|yMatches 'x' OR 'y'.
Expression Syntax: In (n, n1, n2 .....)
Example:
5 In (2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19)
returns -1 (True)
6 In (2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19)
returns 0 (False)
A comparison operator for two regular string expressions.
Expression Syntax: string Like match
string
The text string or property to be matched to.
match
The text string or property to be matched.
Note: Note: The single ? character is handled as a single character match. The single * character is handled as any number of characters match.
Examples:
"quick brown fox" Like Text$
If the text in the first parameter "quick brown fox" is identical to the text in the second parameter; Text$ property then -1 (True) will be returned. If this is not the case then 0 (False) will be returned:
"quick brown fox" Like "the quick brown fox lives here" returns 0
Text$ Like MoreText$
In this example the text in the two text properties are compared. The return values follow the protocol described above.
Logical
The bitwise And operator allows two Boolean expressions to be combined. The statement will be True if both Boolean expressions are True.
Example:
"abc" Like text1$ And "xyz" Like text2$
Returns -1 if text1$ is abc and at the same time text2$ is xyz. If one of the Boolean expressions is False then the expression will return 0.
Example:
_bSimple& Or _bClosed&
Example:
Not _bSimple&
The bitwise And operator allows two Boolean expressions to be combined. The statement will be true if both Boolean expressions are true.
Example:
"abc" Like text1$ And "xyz" Like text2$
Returns -1 if text1$ is “abc” and at the same time text2$ is “xyz”, if one of the Boolean expressions is False then the expression will return 0.
Perform logical negation on a boolean expression, or get two's complement of an integer expression.
Example:
Not(2>1)
As a negation of the true statement 2>1, Not (2>1) will return 0 as the negation of a True statement is False.
The bitwise Or operator allows you to combine two Boolean expressions. The statement will be true if one or another of the Boolean expressions are true.
Example:
"abc" Like text1$ Or "xyz" Like text2$
returns -1 if either one or both linked expressions statements (“abc” Like text1$, “xyz” Like tex2t$) are True. Returns 0 if both Boolean expressions are False.