
Generalises geometry using a variation of the Douglas-Peucker algorithm that is limited by the number of output points.
Property
Number of points*
The number of output points, as a simple value, or as an expression.
Example: 50/100/500
The following examples show the effect of increasing the Number of points value.
Initial Polygon Item:
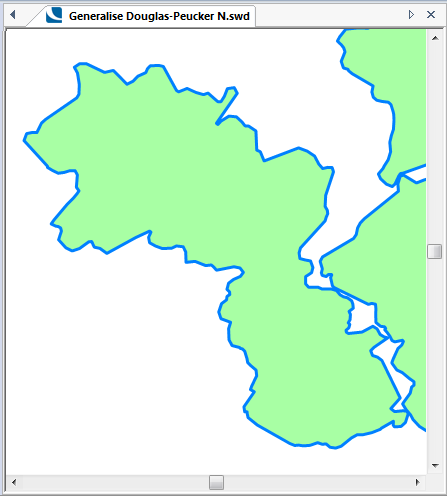
Number of points = 50:
.png)
Number of points = 100:
.png)
Number of points = 500:
.png)
Generalises geometry using the Douglas-Peucker algorithm.
Property
Tolerance*
The Douglas-Peuker algorithm tolerance, as a simple vale, or as an expression.
All vertices in the simplified geometry will be within this distance of the original geometry.
Example: 50/100/300
The following examples show the effect of increasing the Tolerance value.
Initial Polygon Item:
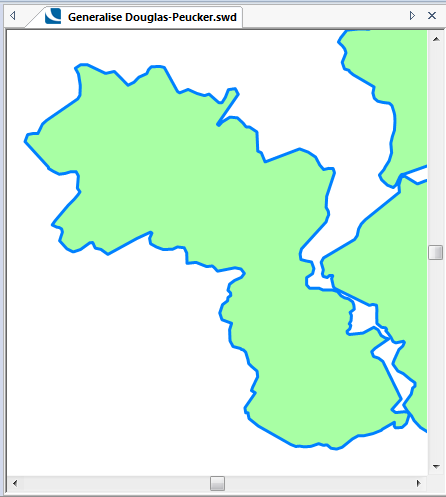
Tolerance = 50:
.png)
Tolerance = 100:
.png)
Tolerance = 300:
.png)
Generalises geometry using the Perpendicular Distance algorithm.
Properties
Repeat*
The number of times to repeat the algorithm, as a simple value, or as an expression.
Example: 4
Tolerance*
The Perpendicular Distance algorithm tolerance, as a simple value, or as an expression.
Example: 50/500/1000
The following examples show the effect of increasing the Tolerance value.
The original map:
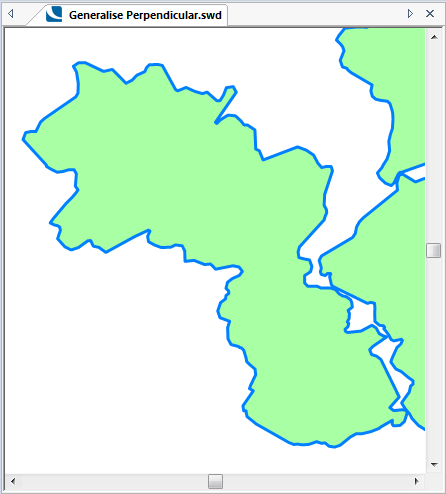
Tolerance = 50:
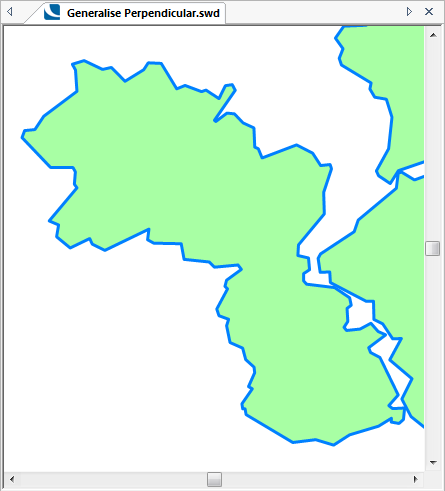
Tolerance = 500:
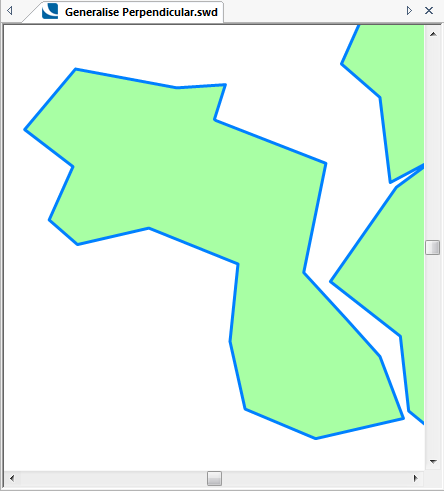
Tolerance = 1000:
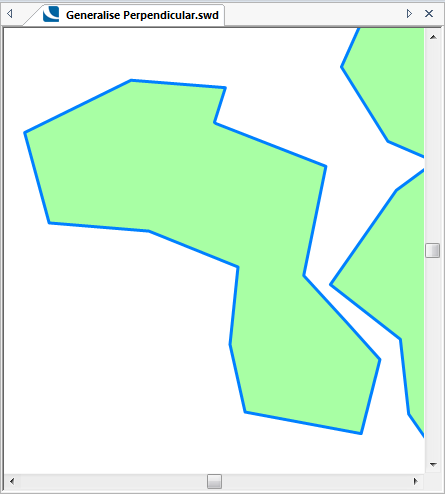
Generalises geometry using the Radial Distance algorithm.
Property
Tolerance*
The Radial Distance algorithm tolerance, as a simple value, or as an expression.
Example: 50/500/1000
The following examples show the effect of increasing the Tolerance value.
The original map:
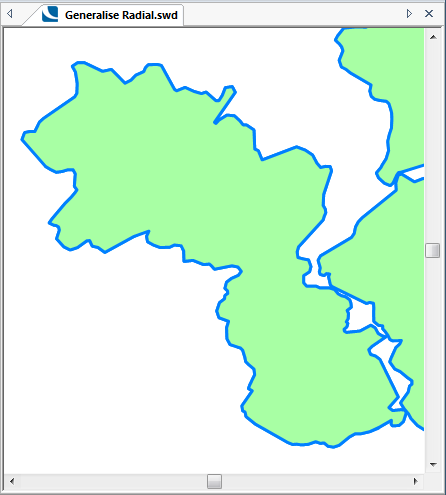
Tolerance = 50:
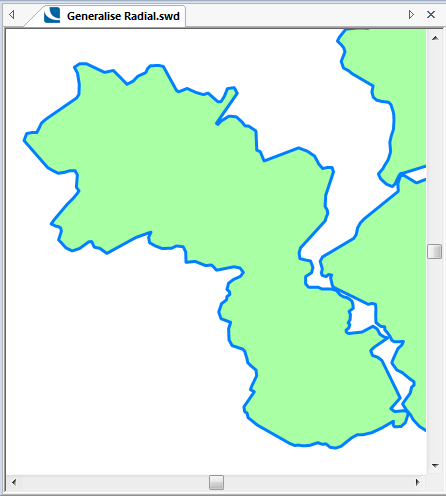
Tolerance = 500:
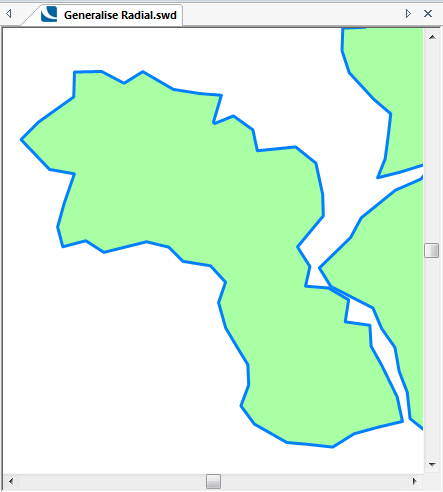
Tolerance = 1000:
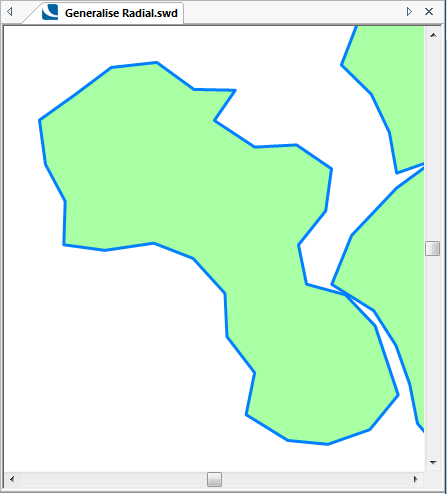
Generalises geometry using the Reumann-Witkam algorithm.
Property
Tolerance*
The Reumann-Witkam algorithm tolerance, as a simple value, or as an expression.
Example: 50/500/1000
The following examples show the effect of increasing the Tolerance value.
The original map:
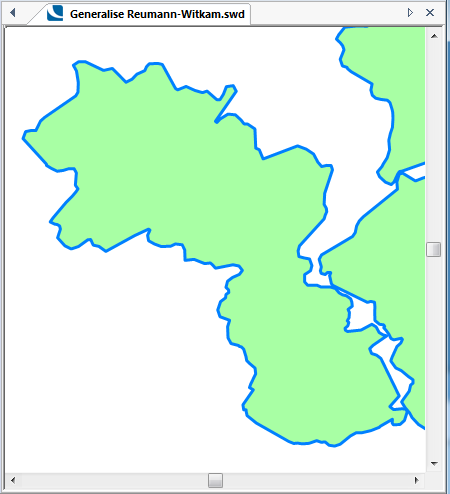
Tolerance = 50:
.png)
Tolerance = 500:
.png)
Tolerance = 1000:
.png)
Removes duplicate items based on an expression.
Property
Expression*
The test expression, e.g. 'FC&' or 'building_type$="industrial"'
As an example consider the following:
The overlay Units contains Industrial and Office buildings:
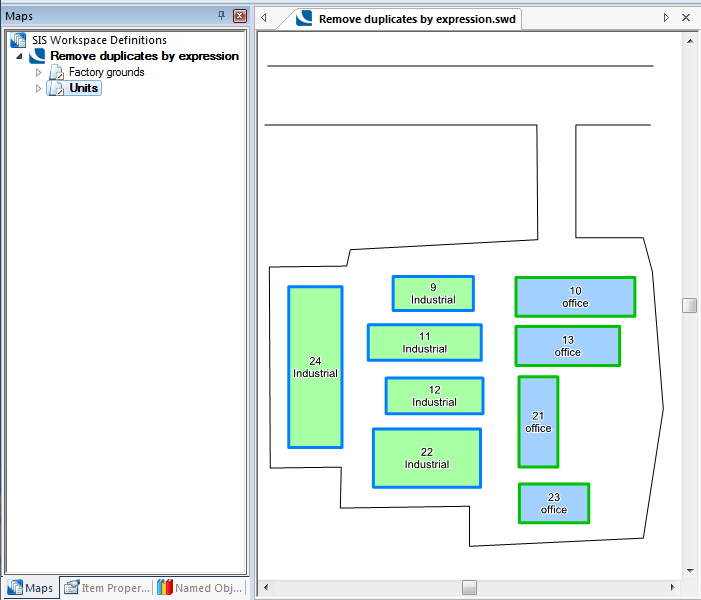
Select the Units overlay:
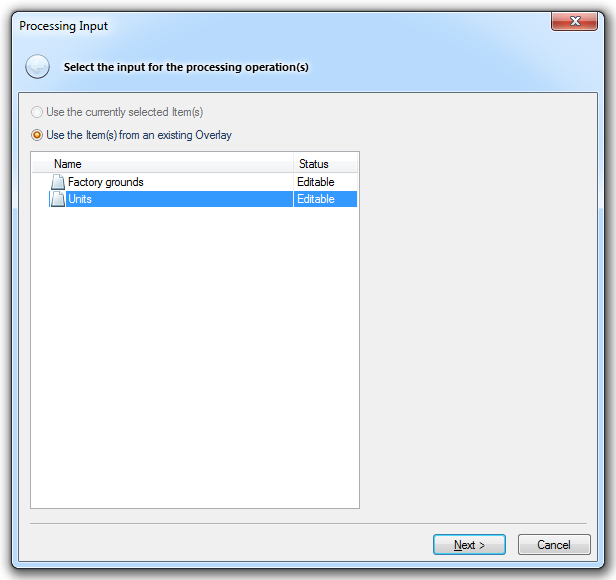
Click Next.
The Processing Operations dialog will be displayed.
Select General > Filter in the left-hand pane and click the right arrow button to add Filter to the right-hand pane.
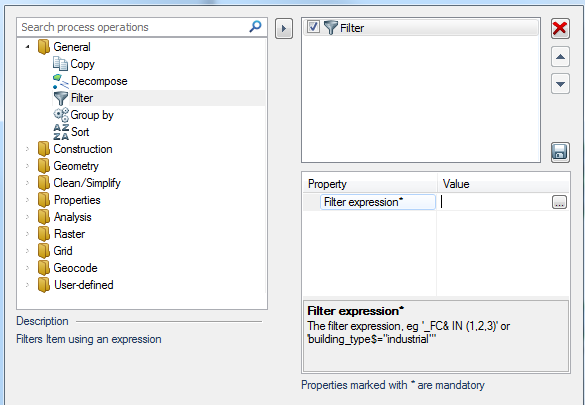
Click the ... button.
The Expression Builder dialog will be displayed:
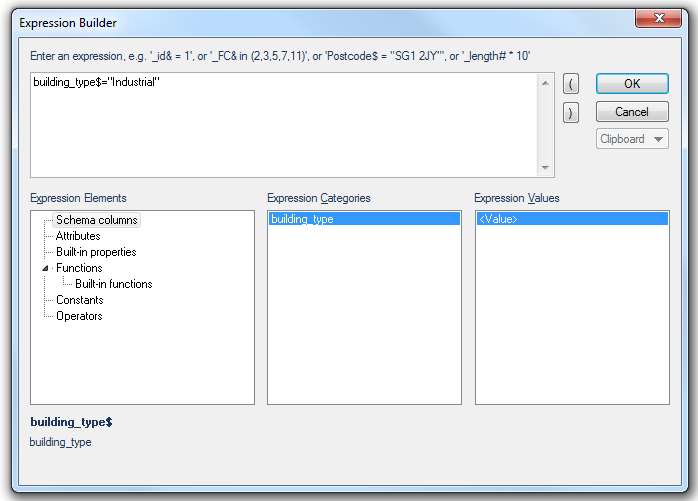
Set the Process command General > Filter to show only the Industrial buildings and click OK.
This will be building_type$="Industrial"
Click OK.
The Filter will now appear in the Processing Operations dialog:
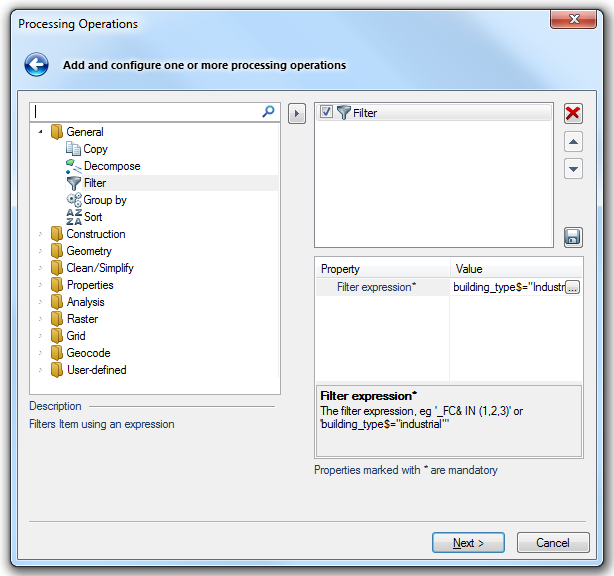
Click Next.
The Processing Output dialog will be displayed. Select the required output and click Finish.
The Processing Input dialog will again be displayed:

Check the Units overlay is still selected and click Next.
The process will run and the final display will be shown:
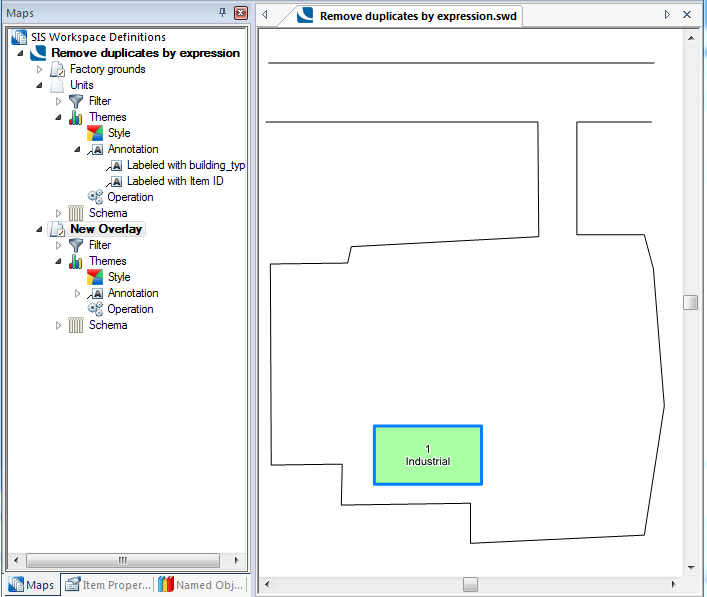
The new overlay will be displayed with all duplicates removed.
Note: The item remaining will be the last item drawn or edited.
Removes duplicate items based on their geometry.
Removes self-intersections, e.g. a bow-tie.
Removes segments shorter than a tolerance.
Property
Tolerance*
The tolerance, as a simple value, or as an expression, e.g. '0.1234' or '0.001234*_length#'
Removes vertices that cause a spike.
Property
Tolerance*
The tolerance, in degrees, as a simple value, or as an expression, e.g. '0.1' or 'Acos(0.999998)*180/3.14'
Removes vertices between straight, or near straight segments.
Property
Tolerance*
The tolerance, in degrees, as a simple value, or as an expression, e.g. '0.1' or 'Acos(0.999998)*180/3.14'.
Simplifies the geometry of an item, so that it matches the OGC 'simple' form (e.g. by removing all self-intersections).
Click here to return to the Run new Process main topic.
Click here to return to the Theme Types dialog - Operation tab - Process topic.
Send comments on this topic.
Click to return to www.cadcorp.com
© Copyright 2000-2017 Computer Aided Development Corporation Limited (Cadcorp).