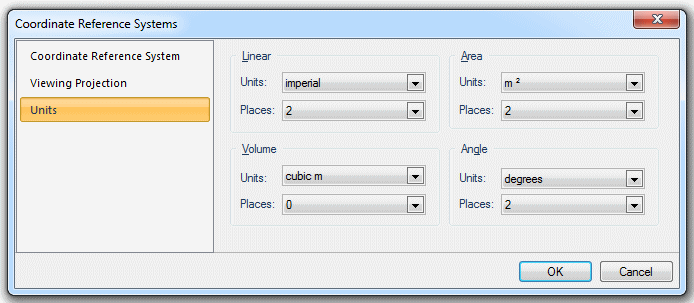
CRS [Home-Map], Units tab, lets you set your preferred units of measurement to any of a range of metric or imperial measures. When entering coordinates or measuring graphics, the preferred units will be used, unless you specify otherwise by appending the unit identifier to the number.
Whenever you type units in SIS, you can:
Example:
If the current set units were millimetres (mm), you could type 4 metres in any of the following ways:
4000
4m
.004km
13.13´
etc.

When you select one of the Units drop-down boxes, you will see a list of the available units. The units are listed using their specifier. You must use this specifier when typing units. For example, included in linear units are millimetres, centimetres, metres and kilometres. When you give dimensions using these units, you type mm, cm, m or km: for example 43mm, .043m.
When the required unit has been selected, select the required precision (number of decimal places) from the Places drop-down box.
Note: The entry before the colon (:) in each case in the following list is the specifier of the unit as shown in the Coordinate Reference Systems dialog, Units tab Linear, Area, Volume and Angle drop-down boxes. The entry in italics following the colon is the EPSG reference. See Note at the bottom of this page.
LinearEPSG: metre
Type: length unit
Notes: also known as International metre
Ref: ISO 1000
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 1
EPSG: kilometre
Type: length unit
Notes:
Ref: ISO 1000
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 1000
EPSG: foot
Type: length unit
Notes: 6 feet
Ref: ISO; 1958
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.3048
EPSG: British yard (Benoit 1895B)
Type: length unit
Notes: G Bomford “Geodesy” 2nd edition 1962; after J S Clark “Remeasurement of the Old Length Standards”; Empire Survey Review, no. 90; 1953
Ref: G Bomford “Geodesy” 2nd edition 1962; after J S Clark “Remeasurement of the Old Length Standards”; Empire Survey Review, no. 90
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.914399204289812
Name: fathom
EPSG: fathom
Type: length unit
Notes: 6 feet
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 1.8288
EPSG: Statute mile
Type: length unit
Notes: 5280 feet
Ref: EPSG
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 1609.344
EPSG: nautical mile
Type: length unit
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 1852
Name: ft (US)
EPSG: US Survey foot
Type: length unit
Notes: used in USA
Ref: EPSG
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.304800609601219
EPSG: Clarke's foot
Type: length unit
Notes: assumes Clarke’s 1865 ratio of 1 British foot = 0.304797265 French legal metres applies to the international metre; used in older Australian, southern African and British West Indian mapping.
Ref:Australian Land Information Group,http://www.auslig.gov.au/geodesy/datums/
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.304797265
Name: Ind.ft (Cla)
EPSG: Indian foot (1975)
Type: length unit
Notes: Indian foot = 0.99999566 British feet (A R Clark 1865); British yard (3 feet) taken to be J S Clark’s 1865 value of 0.9144025m; rounded to 8 significant figures as 1 Ind ft = 0.3048995m; used in India since metrication.
Ref: G Bomford; “Geodesy”; 3rd edition 1975
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.3047995
EPSG: Clarke's link
Type: length unit
Notes: 1/100 Clarke's chain - Assumes Clarke’s 1865 ratio of 1 British foot = 0.304797265. French legal metres applies to the international metre; used in older Australian, southern African and British West Indian mapping.
Ref: Australian Land Information Group, http://www.auslig.gov.au/geodesy/datums/
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.2011661949
EPSG: British link (Benoit 1895B)
Type: length unit
Notes: uses Benoit’s 1895 British yard-metre ratio as given by Bomford as 39.370113 inches per metre; used in West Malaysian mapping.
Ref: G Bomford; “Geodesy”; 3rd edition 1975
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.201167824943759
EPSG: British link (Sears 1922)
Type: length unit
Notes: uses Sears’ 1922 British yard-metre ratio as given by Bomford as 39.370147 inches per metre; used in East Malaysian and older New Zealand mapping
Ref: G Bomford “Geodesy” 2nd edition 1962; after J S Clark “Remeasurement of the Old Length Standards”; Empire Survey Review, no. 90
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.20116767651215526
EPSG: British chain (Sears 1922)
Type: length unit
Notes: uses Benoit’s 1895 British yard-metre ratio as given by Bomford as 39.370113 inches per metre; used in West Malaysian mapping
Ref: G Bomford “Geodesy” 2nd edition 1962; after J S Clark “Remeasurement of the Old Length Standards”; Empire Survey Review, no. 90
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 20.1167824943759
EPSG: British chain (Sears 1922)
Type: length unit
Notes: uses Sears’ 1922 British yard-metre ratio as given by Bomford as 39.370113 inches per metre; used in East Malaysian and older New Zealand mapping
Ref: G Bomford “Geodesy” 2nd edition 1962; after J S Clark “Remeasurement of the Old Length Standards”; Empire Survey Review, no. 90
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 20.11677651215526
EPSG: British yard (Sears 1922)
Type: length unit
Notes: uses Sears’ 1922 British yard-metre ratio as given by Bomford as 39.370113 inches per metre; used in East Malaysian and older New Zealand mapping
Ref: G Bomford “Geodesy” 2nd edition 1962; after J S Clark “Remeasurement of the Old Length Standards”; Empire Survey Review, no. 90
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.914398414616029
EPSG: Indian yard
Type: length unit
Notes: Indian Foot = 0.99999566 British feet (A R Clarke 1865); British Yard (= 3 British feet), taken to be J S Clark’s 1865 value of 0.9144025 metres
Ref: G Bomford “The Re-adjustment of the Indian Triangulation”; Survey of India Professional Paper 28; 1939
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.914398530744441
EPSG: German legal metre
Type: length unit
Notes: used in Namibia
Ref: Chief Directorate Surveys and Land Information; Mowbray; South Africa
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 1.0000135965
EPSG: British foot (Sears 1922)
Type: length unit
Notes: uses Sears’ 1922 British yard-metre ratio as given by Bomford as 39.370147 inches per metre; used in East Malaysian and older New Zealand mapping
Ref: G Bomford “Geodesy” 2nd edition 1962; after J S Clark “Remeasurement of the Old Length Standards”; Empire Survey Review, no. 90
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 0.304799471538676
EPSG: US Survey chain
Type: length unit
Notes: used in USA primarily for public lands cadastral work
Ref: Bureau of Land Management technical bulletin 6 (1973) and Standard Field Tables 8th Edition (1956)
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 20.1168402336805
EPSG: US Survey link
Type: length unit
Notes: used in USA primarily for public lands cadastral work
Ref: Bureau of Land Management technical bulletin 6 (1973) and Standard Field Tables 8th Edition (1956)
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 20.1168402336805
EPSG: US Survey mile
Type: length unit
Notes: used in USA primarily for public lands cadastral work
Ref: Bureau of Land Management technical bulletin 6 (1973) and Standard Field Tables 8th Edition (1956)
Source: EPSG
Unit: metre
Multiplication factor: 1609.34721869444
EPSG: degree
Type: angular unit
Notes:p/180
Source: EPSG
Unit: radian
Multiplication factor: 1.74532925199533E-02
EPSG: radian
Type: angular unit
Notes: SI standard unit
Ref: ISO 1000
Source: EPSG
Unit: radian
Multiplication factor: 1
EPSG: degree minute second
Type: angular unit
Notes: degrees<space>arcminutes<space>arcseconds
degrees - integer
arcminutes - integer
arcseconds - real
Source: EPSG
Unit: radian
EPSG: grad
Type: angular unit
Notes:p/180 - in France also abbreviated as "gr"
Source: EPSG
Unit: radian
Multiplication factor: 0.0157079633267949
EPSG: degrees decimal minutes
Type: angular unit
Notes: degrees<space>decimal minutes
degrees - integer
decimal minutes - integer
Source: EPSG
Unit: radian
Name: Tubo
EPSG: tubo
Type: real unit
Notes: 3 feet x 6 feet
Note: The European Petroleum Survey Group (EPSG) was formed in 1986. It disseminates information to improve oil industry survey practices and procedures. From this group, the geodesy working group maintains a relational database of geodesy parameters which is used in SIS. The European Petroleum Survey Group has compiled and distributes the various geodetic and cartographic coordinate system parameters. The coordinate systems in this database are listed in SIS.
SIS uses version 8.5 of the EPSG CRS database.
Send comments on this topic.
Click to return to www.cadcorp.com
© Copyright 2000-2017 Computer Aided Development Corporation Limited (Cadcorp).