Types of 3D data
1. Surface
Surfaces are three-dimensional planar items which have an area but no volume. (e.,g a public park)
Surface items can be created in three different ways.
Method 1:
- Select the LineString or closed MultiLineString item(s).
- Use Create > 3D > Extrude.
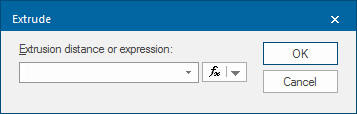
- Supply a distance, or an expression that will be used to calculate the extrusion distance.
- To use an expression click the
 button drop-down and select Edit an Expression to display the Expression Builder dialog.
button drop-down and select Edit an Expression to display the Expression Builder dialog.
Method 2:
- Select the Polygon item(s).
- Use Triangulate (Create > 3D) or the local command Convert to 3D Surface.
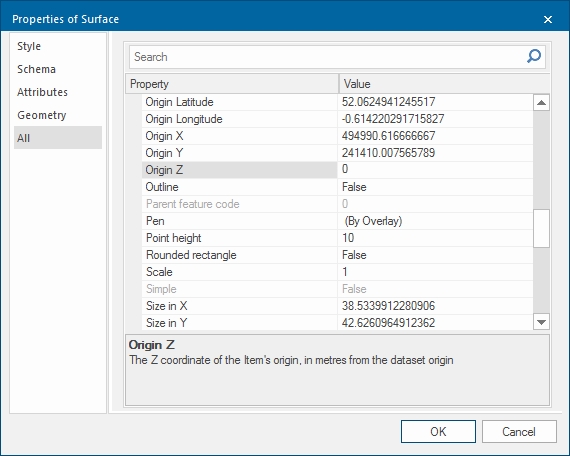
- Assign a height to the area using the Properties of Surface dialog, Origin Z option.
Method 3:
- Select the LineString or closed MultiLineString item.
- Click on one of the grab handles.
- Type in comma, comma and a numerical value for Z which stands for height (e.g. ,,50), then press Enter. The point on screen will be given this height and if viewed in a 3D window, the surface will appear curved.
Note: Before moving on to the next step, move the grab handle position slightly. (Why is this done?)
2. Solids
Solids are three-dimensional solid items which have volume. (e.g a rectangular building)
Creating a solid item
- Select the LineString or closed MultiLineString item.
- Extrude the area using Create > 3D > Extrude.
- Supply a height to which these items will be extruded.
3. Grids
Grids are raster items where each pixel or cell has a colour value that corresponds to a numerical value.
This numerical value can represent various different scenarios - for example, the number of people living in the area represented by the cell (population density); the reflected sunlight produced from a certain type of vegetation represented by the cell (seen in certain types of satellite images); or the height above sea level represented by the cell.
This last option is the starting point for a type of Digital Terrain Model (DTM).
TIP: For more information on Grids, see What are Grid items?