Measure Distance
Measure Distance measures and reports the distance between positions (or alternatively the cumulative distance from one position) through a series of subsequent positions to the last position chosen. The positions can be three-dimensional.
Select Home > Measurement > Distance:
This opens the Measure Distance dialog:
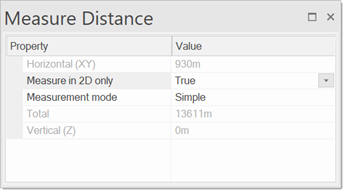
The Horizontal (XY) and Vertical (Z) fields give a constant read-out of distances from the first point to the subsequent points. The horizontal distance is the direct distance between the points on the XY plane. The vertical distance is the Z height.
When you click the point(s) to measure to, the distance between them is displayed as a running total in the Total field.
All distance values are reported in the current units and to the number of decimal places settings as set by CRS Coordinate Reference Systems dialog, Units tab.
Measure in 2D is a property to control or convert all measurements to 2D; this removes the unwanted side-effects of snapping on 2D and 3D features.
There are three Measurement modes to choose from when using Measure Distance:
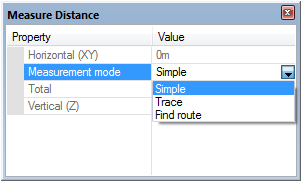
- Simple - measures the direct distance between any positions in the map window, press Enter or double-click to finish.
- Trace - measures the distance between two positions on a linear feature. This could be a LineString item, a closed LineString item or a link item, or the perimeter of a Polygon item. If you are measuring a closed item (LineString or Polygon item), the shortest path between the two points is taken.
- Find route - carries out the same operations as Trace but on multiple items, if they are intersecting. If used on a single item which self-intersects, it does not trace the item, but uses intersections as turning points.
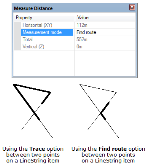
-
Press Enter or double-click to finish the Measure Distance command.

An  Information box shows the distance, the units and number of decimal places are as set in the Coordinate Reference Systems dialog. To change the units or number of decimal places go to CRS Units tab.
Information box shows the distance, the units and number of decimal places are as set in the Coordinate Reference Systems dialog. To change the units or number of decimal places go to CRS Units tab.
Click the Copy to clipboard button to copy the value to the Windows clipboard as text. When pasted back, it is placed as a text item at the centre of the current map window, or it can be pasted into a text dialog box or a spreadsheet, as appropriate.
Click the x button in the  Information box to dismiss the message.
Information box to dismiss the message.
How distances are calculated
- If the current Coordinate Reference System is spherical (i.e. Latitude/Longitude), then Great Circle distances are measured.
The Great Circle distance is calculated accurately in radians using the haversine expression. The angular distance is then converted to metres using an approximation for the local radius of curvature of the Earth. - If the current Coordinate Reference System is Cartesian, then the 3D straight line distance is measured.
- If the Coordinate Reference System is Transverse Mercator, the measuring is done within the Coordinate Reference System. This means the answer will not take account of the Coordinate Reference System distortions.