A Coordinate Reference System is a method of projecting positions in the world onto screen/paper.
The surface of the Earth is curved, but paper is flat. These two facts mean that paper maps will always be slightly distorted. Different Coordinate Reference Systems are designed to minimise the distortion in different ways. Some Coordinate Reference Systems show orientation accurately, some show areas accurately etc.
See Coordinate Reference Systems for the available Coordinate Reference System types. Coordinate Reference System objects can be specified using Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Well-Known-Text strings.
Cadcorp SIS lets you create Coordinate Reference System objects and save them in Named Object Libraries using names. You can also use implicit coordinate reference systems. The DefineNolObject and GetImplicitNolObject API methods use implicit coordinate reference systems to create and query Coordinate Reference System objects. The format of the implicit string is Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Well-Known-Text. See the OpenGIS Simple Features Specification for more information.
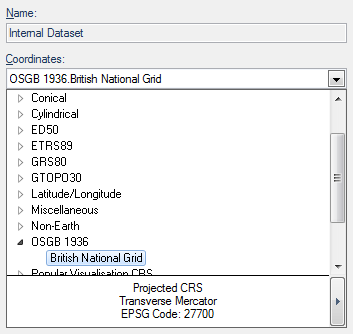
You can see Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Well-Known-Text strings for Coordinate Reference System objects using CRS [Home-Map] to display the Coordinate Reference Systems dialog.
The Coordinate Reference System dialog can be displayed from the Overlays dialog Coordinates drop-down list and clicking on the right button at the bottom:

The Coordinate Reference System dialog has three tabs:
Origin
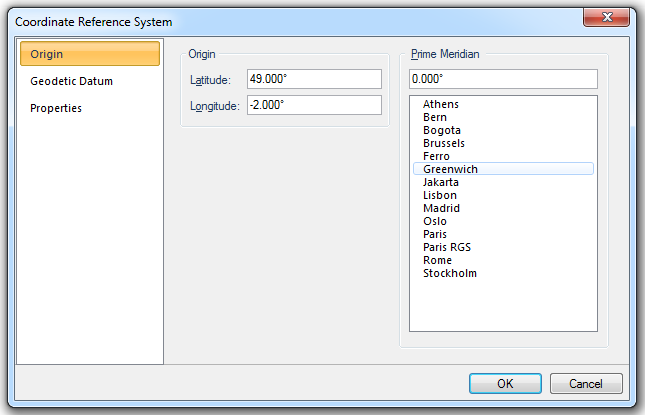
Origin
Latitude
The latitude of the origin of the coordinate reference system.
Longitude
The longitude of the origin of the coordinate reference system.
Prime Meridian
Prime Meridian that the coordinate reference system is based on, relative to Greenwich.
A list of Standard Prime Meridians is given.
Geodetic Datum
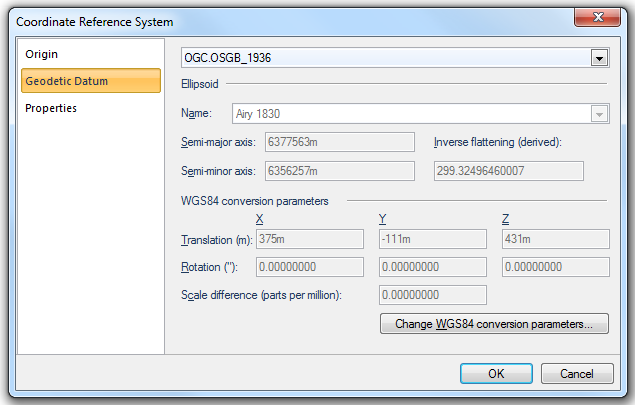
Name
A Geodetic Datum (sometimes called simply a Datum) models the sea-level surface more accurately than an ellipsoid. SIS contains equations for transforming points between Geodetic Datums, or you can make your own Geodetic Datums by applying seven conversion parameters to the WGS84 standard Geodetic Datum.
Ellipsoid
Name
Reference ellipsoid name, i.e. Airy 1830 in this example.
Semi-major axis
Distance from centre of ellipsoid to any point on the equator in metres.
Semi-minor axis
Distance from centre of ellipsoid to either pole in metres.
Inverse flattening (derived)
Inverse flattening value.
WGS conversion parameters
Shift X/Y/Z
Shift between WGS84 and Geodetic Datum.
Rotate X/Y/Z
Rotate between WGS84 and geoid, in seconds of an arc.
Correction (parts per million)
Correction scale in parts per million.
Properties
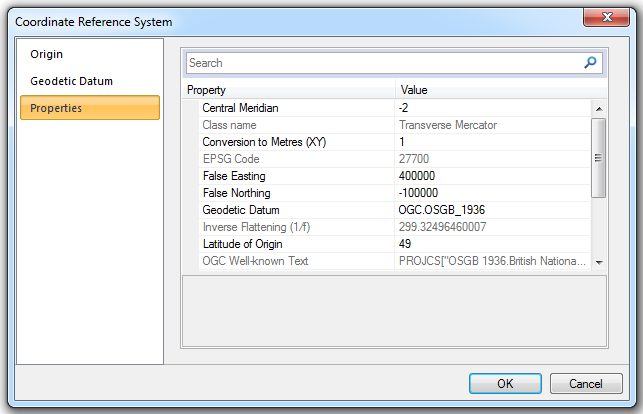
The Properties tab displays all properties of the coordinate reference system.
Send comments on this topic.
Click to return to www.cadcorp.com
© Copyright 2000-2017 Computer Aided Development Corporation Limited (Cadcorp).