Spatial Analysis- Boolean Operations
Boolean operations allow SIS Desktop 9 to investigate the spatial relationships of two or more simple geometries.
Boolean operations allow the
- Union of multiple geometries into a single geometry item
- Cookie-cutting a single intersection item
- Subtracting multiple geometries from a single geometry or
- Keeping the symmetric difference between the union and the intersection of the same geometries.
You can also dissolve (union) geometries based on their associated attribute values.
The following example shows a Boolean intersection:
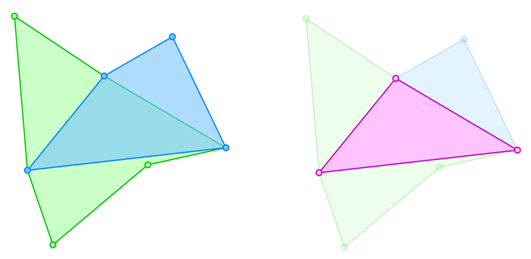
Boolean algebra (or Boolean logic) in Cadcorp SIS Desktop is a logical check of the spatial relationship between different simple geometries.
Cadcorp SIS Desktop can test groups which contain area, line, and point geometries.
All Boolean operations in Cadcorp SIS Desktop result in a single or one multi-geometry item. If the items in the test group have different attributes, Cadcorp SIS Desktop will prompt for the item whose properties should be retained.
Boolean logic is based on the basic operations, namely conjunction (Intersect), disjunction (Union) and negation (Subtract).
A Boolean disjunction (Union) is true for all geometries contained in the test group. The resulting item will be either a single geometry (where the same geometry types can be merged) or a multi-geometry (when the geometry elements are spatially separated or different geometry types have been tested together).
A Boolean conjunction (Intersect) is based on the logical AND statement. A spatial union will create a new geometries whose extent is the geometric intersection of all items in the test group. In a test group containing the areas A, B, and C, only the intersection of all three areas will become the product of the Union operation. Where only two of the three areas intersect, the Boolean conjunction is not true.
SIS Desktop 9 requires the selection of a single item for the Boolean negation (Subtract). The geometries of all other items in the test group will be subtracted from this geometry.
The following figure shows Boolean operations in SIS Desktop 9:
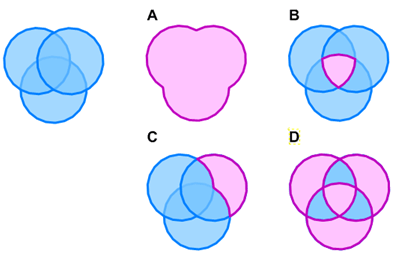
A = Union
B = Intersection
C = Subtract