.gif) /
/ %20button%20(100).gif) Query Builder
Query Builder.gif) /
/ %20button%20(100).gif) Query Builder
Query Builder
.gif) Query Builder constructs a data query to find items in an overlay.
Query Builder constructs a data query to find items in an overlay.
Note: For the fastest query responses on database overlays use the Run the query using: Database filtering option in the Query Overlay dialog. This uses the database for performing the query.
See Querying Spatial Database Spatial Overlays
Query Builder [Home-Map] or [Table-Sort & Filter] helps you look for items on an overlay. You can look for:
When it has found matching items, the Query Builder can either:
You can also have the query set a filter or spatial filter, so that you can use the items found by the query as the basis for further operations. See Spatial testing: Spatial Filter.
Before you start Query Builder, select an item or items if you want to look for other spatially-related items.
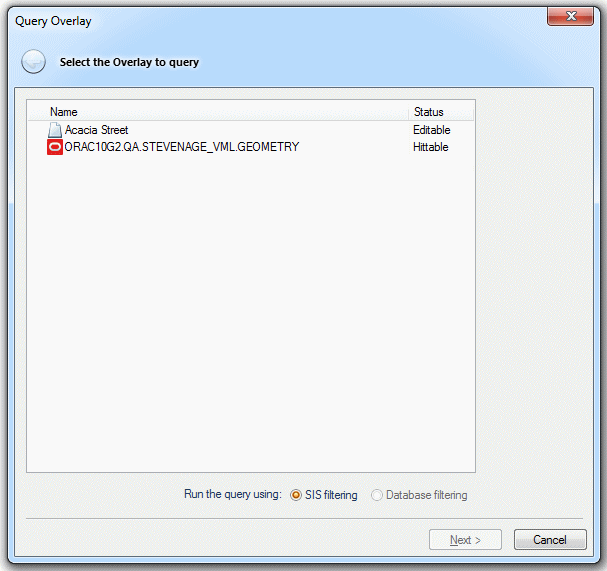
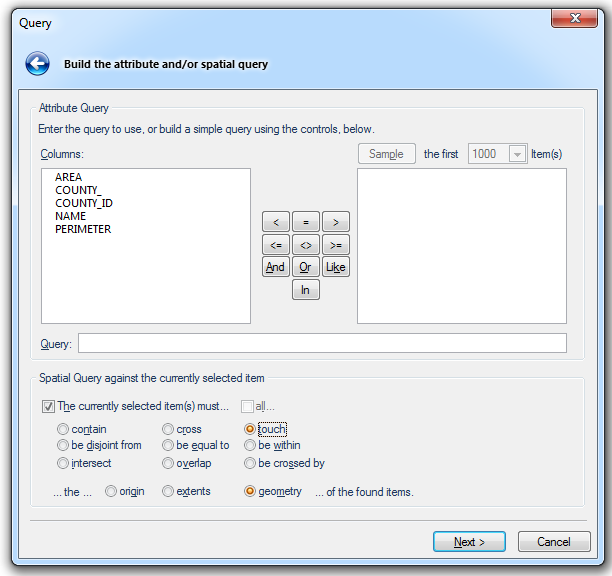
The Query dialog will be displayed:
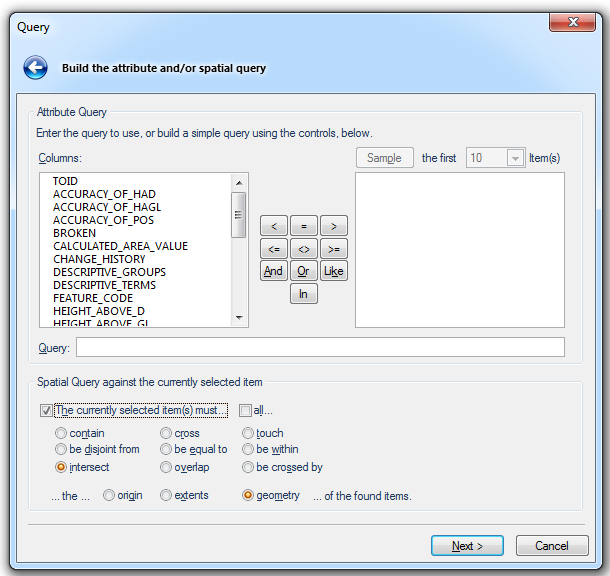
Enter the details of the attribute query and/or spatial query you wish to carry out.
Note: The Spatial Query against the currently selected item tickbox and options will only be available if items are selected on the overlay.
Attribute Query
Columns - This pane shows the columns in the overlay schema
The Function keypad
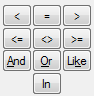
Examples of the use of the keys:
 Less than
Less than
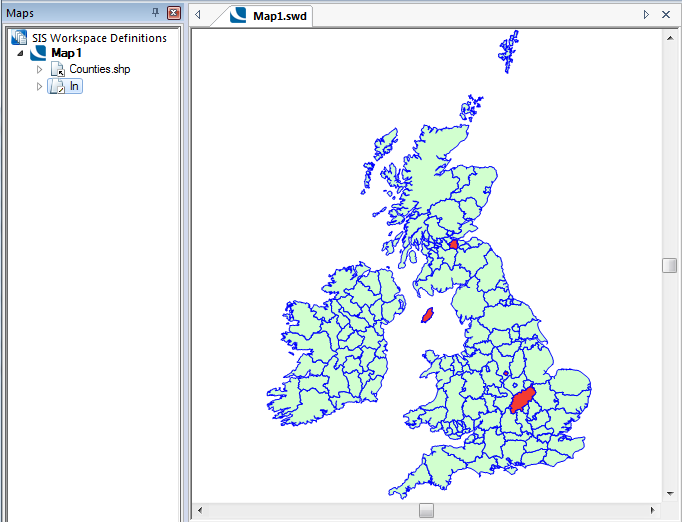
Example Query: CALCULATED_AREA_VALUE& < 1000
Returns all areas less than 1000 in current units.
 Equal to
Equal to
Example Query: CALCULATED_AREA_VALUE& = 1000
Returns all areas equal to 1000 in current units.
 Greater than
Greater than
Example Query: CALCULATED_AREA_VALUE& > 1000
Returns all areas greater than 1000 in current units.
 Less than or equal to
Less than or equal to
Example Query: CALCULATED_AREA_VALUE& <= 1000
Returns all areas less than or equal to 1000 in current units.
 Not equal to
Not equal to
Example Query: CALCULATED_AREA_VALUE& <> 1000
Returns all areas not equal to 1000 in current units.
 Greater than or equal to
Greater than or equal to
Example Query: CALCULATED_AREA_VALUE& >= 1000
Returns all areas greater than or equal to 1000 in current units.
The And, Or, Like and In keys
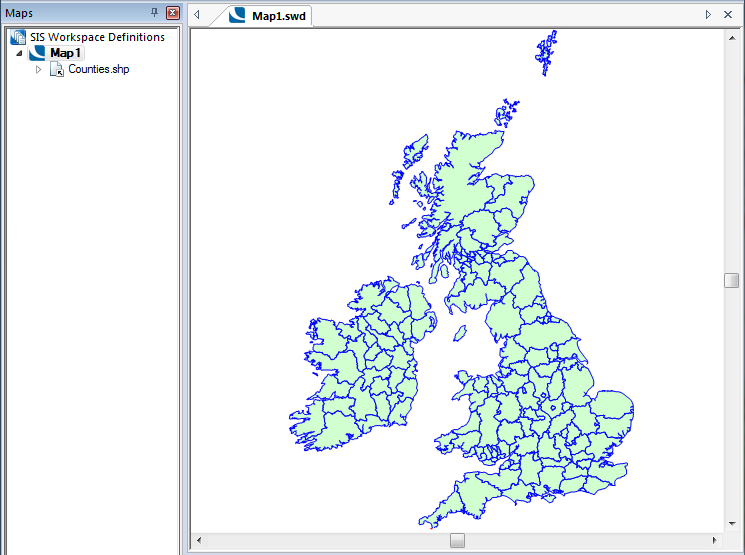
Using Counties.shp as an example:
 And
And
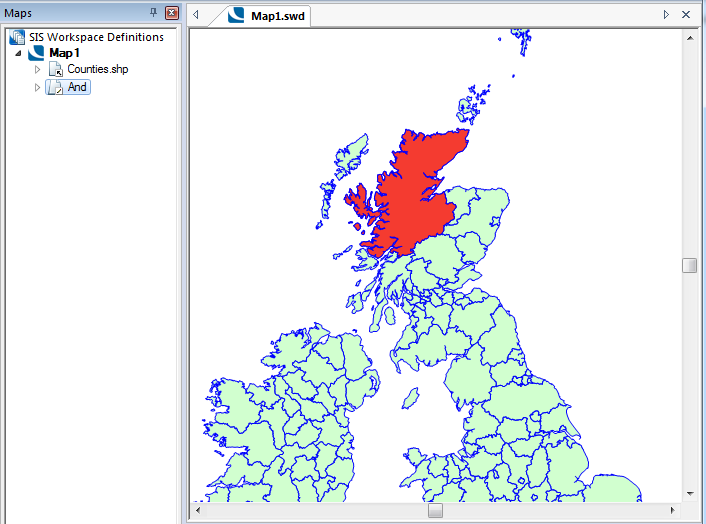
Example Query: NAME$ = "Highland" And COUNTY_ID# = 5
Returns Highland, providing the name (Highland) and the county id match:
 Or
Or
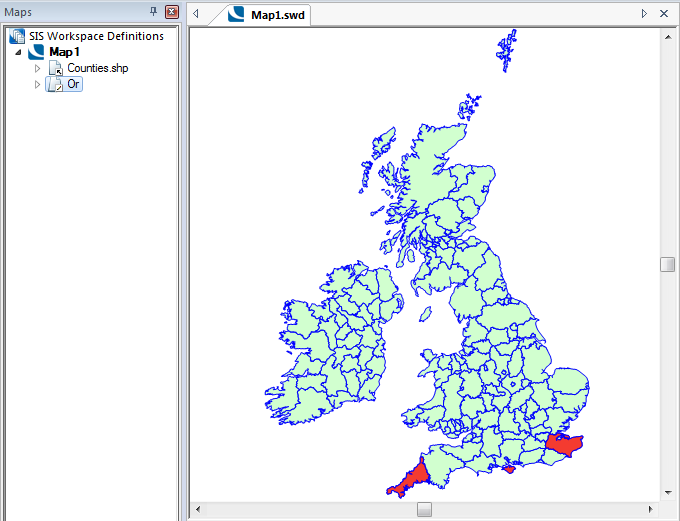
Example Query: NAME$ = "Cornwall" Or NAME$ = "Isle of Wight" Or NAME$ = "Kent"
Returns Cornwall, Isle of Wight and Kent:
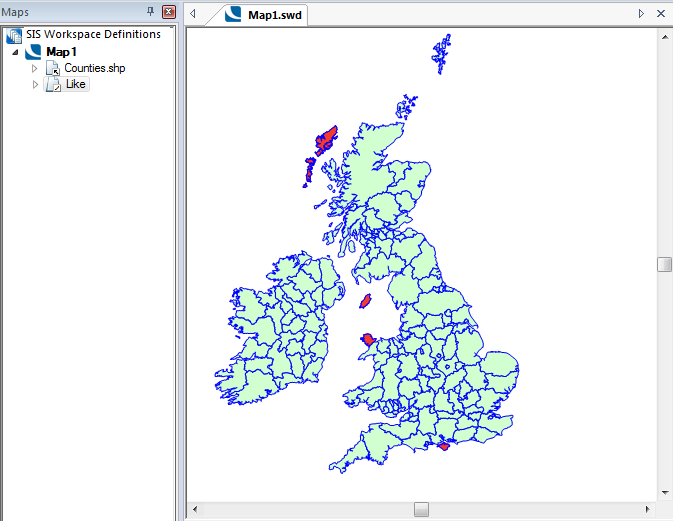
Example Query: NAME$ Like ‘Isle’
Note: If the Database filtering option has been chosen in the Query Overlay dialog it is necessary to add wildcard characters, otherwise the query will not return any output. Therefore, in this example the Like query should be ‘NAME Like ‘%Isle%’ in order to return the same output, also note the $ character is omitted due to using database data.
Returns names containing Isle, i.e. Western Isles, Isle of Man, Isle of Anglesey, Isle of Wight.
 In
In
The In function reduces the need to use multiple OR functions.
Example Query: NAME$ In("Northhamptonshire","West Lothian","Isle of Man","Derby" )
Returns Northhamptonshire, West Lothian, Isle of Man and Derby:
Sample button
.png)
Click the Sample button to display the first number of item(s), as selected in the drop-down in a range of 1 to 1000, for the selected column.
Typical values - This pane shows the values that
See the Geometry Tests topic for a further explanation of the OGC specified method for computing spatial relationships between geometries.
all... - Tick if all of the selected items have to pass the test, or untick if any one will be enough.
The following is an example of the dimensionally extended nine-intersection matrix (DE-9IM) for the case where (a) and (b) are two Polygons that overlap.
contain - The interior of the found item must be strictly inside the current item."T****F*"
cross - If the items are LineStrings, then they must intersect without being tangential. Otherwise, their interiors must intersect, with the current item going outside the found item.
LineStrings: "0********"
Other: "T*T******"
touch - The items interiors must be disjoint, AND their boundaries must intersect.
"FT*******" or "F**T*****" or "F***F****"
be disjoint from - The items must be completely separate, with daylight between them.
"FF*FF****"
be equal to - The two items' geometry must be the same.
"TFFF*FFF*"
be within - The interior of the current item must be strictly inside the found item.
"T*F**F***"
intersect - The items must not disjoint, so they must have a point in common. This is the fastest, and most common test.
not "FF*FF****"
overlap - If the two items are LineStrings, then they must be tangential, and neither should contain the other. Otherwise, their interiors must intersect, with neither containing the other.
LineStrings: "1*T***T**"
Other: "T*T***T**"
be crossed by - If the items are LineStrings, then they must intersect without being tangential. Otherwise, their interiors must intersect, with the found item going outside the current item.
LineStrings: "0********"
Other: "T*****T**"
...the... - ...of the found itemsorigin - This is the origin of the Items to be queried. This is normally (but not always) the approximate centre of a Polygon or the starting point of a LineString.
extents - This means the imaginary bounding box around the item’s geometry, using the minimum and maximum x/y values of the item.
geometry - This is the outline of the Item. This is the slowest, but most accurate mode.
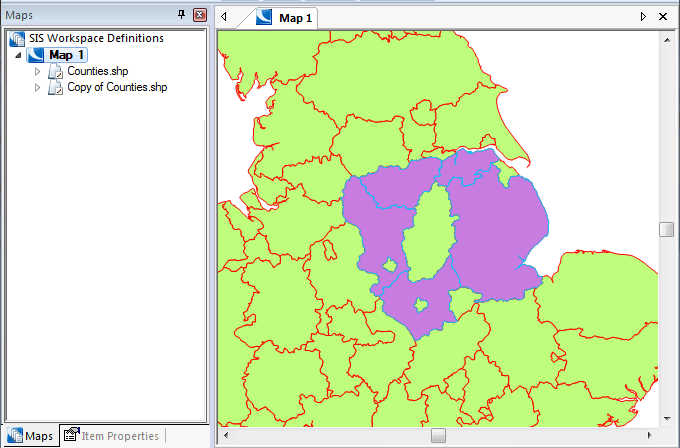
The above example shows a query build that filters the overlay to display data that intersects the currently selected item.
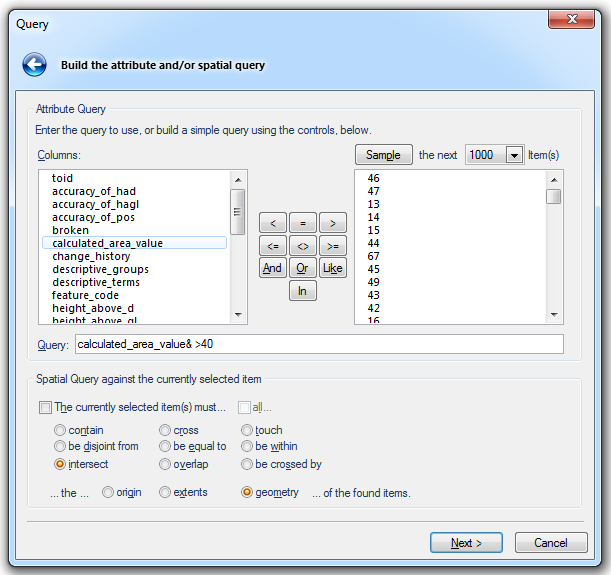
You can use the function keypad directly to input an operator or type a query directly into the Query field.
If you selected an item or items before starting the query, you can create a spatial query using the selection. Check the tickbox next to The currently selected item(s) must… and then choose the test required.
Choose also whether you want to test against the origin, extents, or geometry of the found items.
The geometry of an item is:
- for a Polygon item, its area;
- for a LineString item, its length;
- for a Point item, its x and y coordinates.
Some of the spatial tests operate differently depending on which of the origin, extents, or geometry is used.
Check the all… tickbox if all the selected items must pass the test, or leave it blank if at least one selected item must pass.
On completion of the dialog click Next.
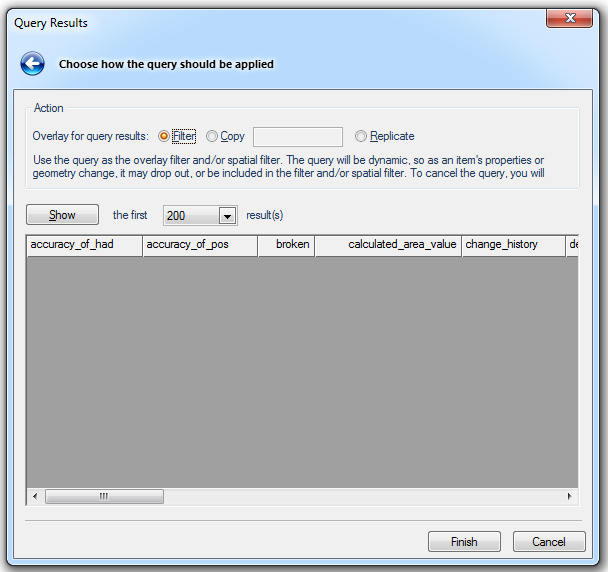
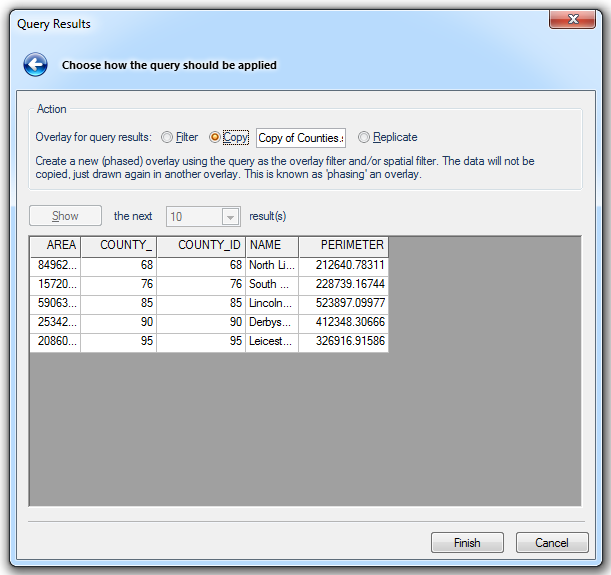
Select from the three Action - Overlay for query results options:
Filter - Use the query as the overlay filter and/or spatial filter. The query will be dynamic, so as an item's properties or geometry change, it may drop out of, or be included in the filter and/or spatial filter.
Copy - Create a new (phased) overlay using the query as the overlay filter and/or spatial filter. The data will not be copied, just drawn again in another overlay. This is known as 'phasing' an overlay.
The name of the overlay to be copied will be shown in the text box.
Replicate - Copy the query results into a new 'Internal' overlay, for further processing. The connection to the source data will be lost.
Show the first/the next xxx result(s)
Click Show for a preview of the first selected number of results. For example:
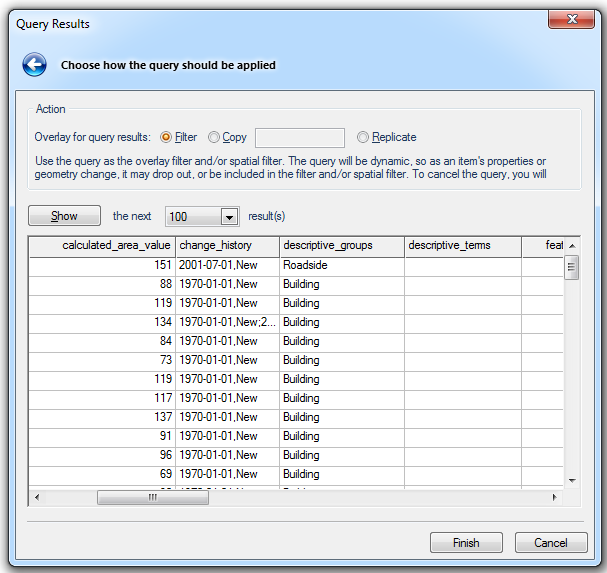
Show the next xxx result(s) will now be displayed. Select the required number of results and click Show to display the next results.
Click Finish to complete the query.

Top of page