With external or user data displayed on screen, you can access information on:
This topic describes how to access this information.
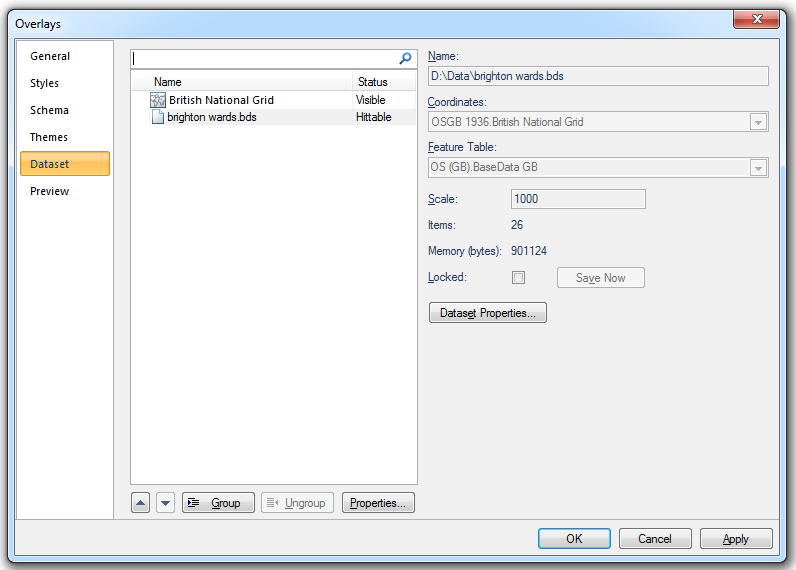
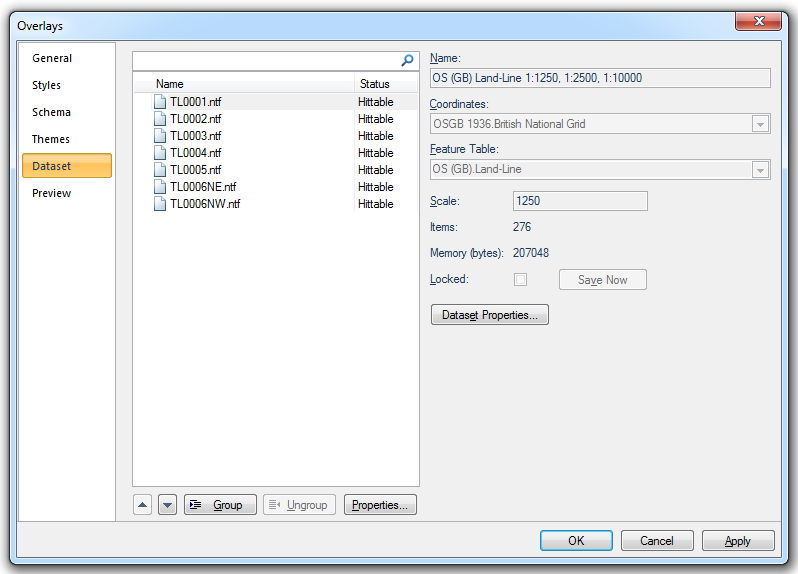
The Dataset tab of the Overlays dialog contains information about the datasets included as overlays in the current SWD. Some of these settings can be changed from here.

The Dataset tab displays:
Coordinate Reference System dialogs which has three tabs:
Origin
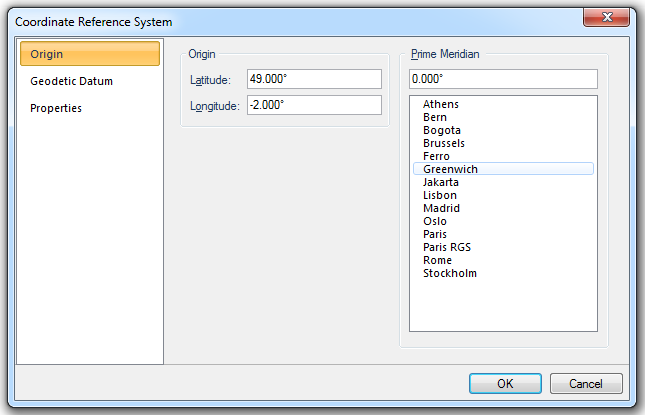
Origin
Latitude
The latitude of the origin of the coordinate reference system.
Longitude
The longitude of the origin of the coordinate reference system.
Prime Meridian
Prime Meridian that the coordinate reference system is based on, relative to Greenwich.
A list of Standard Prime Meridians is given.
Name
A Geodetic Datum (sometimes called simply a Datum) models the sea-level surface more accurately than an ellipsoid. SIS contains equations for transforming points between Geodetic Datums, or you can make your own Geodetic Datums by applying seven conversion parameters to the WGS84 standard Geodetic Datum.
Ellipsoid
Name
Reference ellipsoid name, i.e. Airy 1830 in this example.
Semi-major axis
Distance from centre of ellipsoid to any point on the equator in metres.
Semi-minor axis
Distance from centre of ellipsoid to either pole in metres.
Inverse flattening (derived)
Inverse flattening value.
WGS84 conversion parameters
Translation (m) X/Y/Z
The difference between the X/Y/Z values of a point in the target and source coordinate reference systems.
Rotation (") X
The angular difference (about the X axis, viewed from the origin) between the Y and Z axes directions of target and source coordinate reference systems (in seconds of an arc).
Rotation (") Y
The angular difference (about the Y axis, viewed from the origin) between the X and Z axes directions of target and source coordinate reference systems (in seconds of an arc).
Rotation (") Z
The angular difference (about the Z axis, viewed from the origin) between the X and Y axes directions of target and source coordinate reference systems (in seconds of an arc).
Scale difference (parts per million)
The scale difference increased by unity equals the ratio of the length of an arbitrary distance between two points in target and source coordinate reference systems..
Change WGS84 conversion parameters...
Press the Change WGS84 conversion parameters... button to display the Change WGS84 conversion parameter variants information screen:
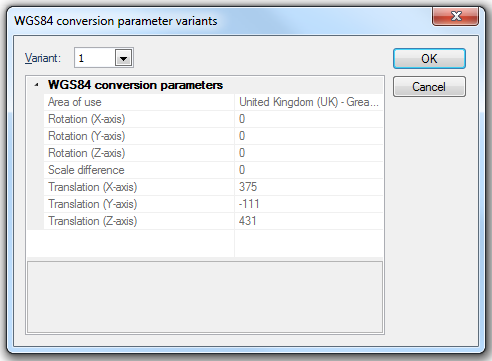
Variant
The variant of the WGS84 conversion parameters. Higher numbers indicate more recent variants.
Click OK.
The WGS84 conversion parameter variants screen will be displayed:
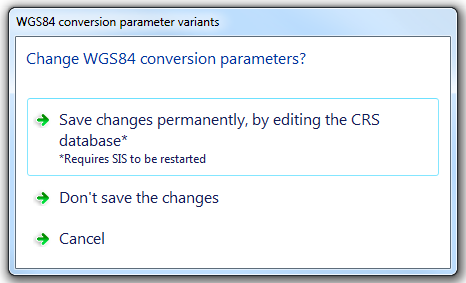
Select Save changes permanently, by editing the CRS database, Don't save the changes or Cancel.
Note: If you select Save changes permanently, by editing the CRS database then SIS will have to be closed and restarted to register the change.
Properties
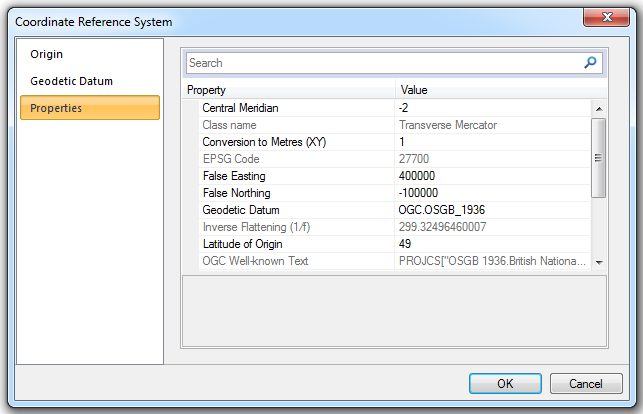
The Properties tab displays all properties of the coordinate reference system.
Click on OK in any of the three Coordinate Reference System dialog tabs to return to the Overlays dialog.
- Feature Table - (can be changed if this is a user dataset) the feature table used for feature-coded items in this dataset. Feature-coded items get information about their feature code either from this feature table, or, if set, their own Feature Table property.
- the dataset Scale (this can be changed).
- the number of graphical Items it contains.
- the amount of computer Memory (bytes) it takes up.
- the Locked status indicated by the checked Locked tickbox (if this is a BDS file).
- Properties of the overlay, such as its pen and brush, its status, at what scales it is drawn, and so on.
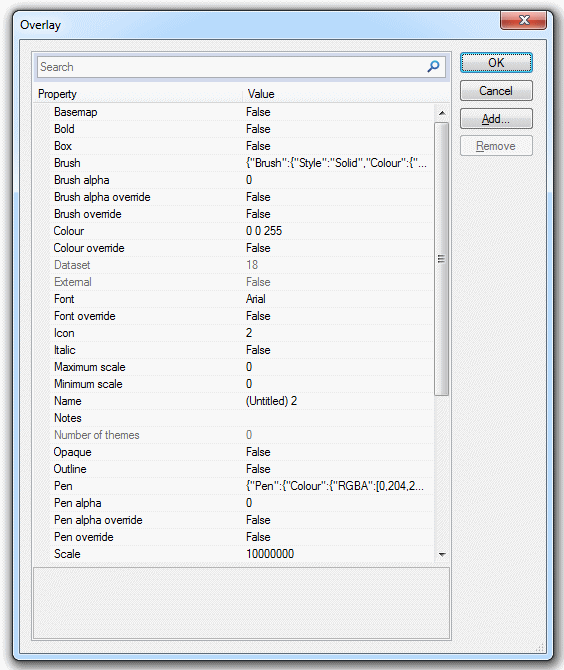
- the dataset’s Dataset Details. A typical dataset details dialog may look like this:
In the case of a BDS, you will see and can change the Coordinates system projection and the scale. Other information is shown, and you can also access the overlay’s properties.
This same information is also accessed in the Maps Control Bar and from an overlay’s local command Dataset > Properties....
The Maps Control Bar shows a tree structure for all the SWDs in the current session, showing the overlays they contain and the contents of those overlays.
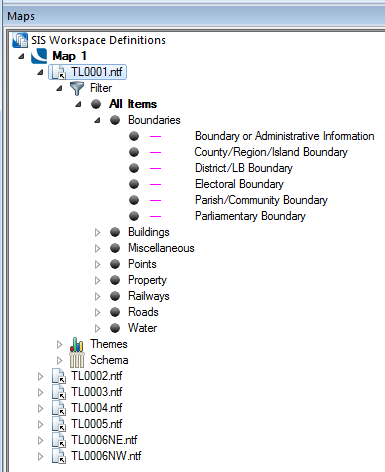
The local menu for each overlay includes the Properties... command, this displays the Overlays dialog, the Dataset tab gives the information on the dataset to which the overlay refers:
Measure Position [Home-Measurement] returns a position relative to the current axes.
.gif) Measure Distance
Measure DistanceMeasure Distance [Home-Measurement] measures and returns the distance between points, or alternatively the cumulative distance from one point, through a series of subsequent points, to the last point chosen.
.gif) Measure Area
Measure AreaMeasure Area [Home-Measurement] measures and returns the area of a "fence" Polygon.
Use Measure Angle [Home-Measurement] measures and returns the angle formed between two LineString items or LineString item segments. If the LineString items are not connected, you are given the angle which would be formed if they were extended to meet.
.gif) Measure Geometry Length
Measure Geometry LengthMeasure Geometry Length [Home-Measurement] measures and returns the total length of the selected item(s).
.gif) Measure Geometry Area
Measure Geometry AreaMeasure Geometry Area [Home-Measurement] measures and returns the area value of the selected item(s).
.gif) Measure Geometry Volume
Measure Geometry VolumeMeasure Geometry Volume [Home-Measurement] measures and returns the total volume of the selected items.
.gif) Measure Geometry Radius
Measure Geometry RadiusMeasure Geometry Radius [Home-Measurement] measures and returns the radius of any selected circle, arc or curve.
.gif) Point-to-point
Point-to-pointPoint-to-point [Analysis-Route Finding] finds the distance between two points on LineString and Link items and the perimeter of Polygon items. You will see a route drawn between the points.
To find a grid reference, use Zoom Grid Reference [Home-Zoom]. This displays a Grid Reference dialog into which you can type a grid reference. SIS zooms the map window to show the position, if it exists.
National Grid references specify an extent on the map base. They can be used to find and zoom into any area of your map base, whether you are viewing Ordnance Survey data or any other.

SIS zooms the map window to show the position, if it exists. The area shown depends on how precisely you specified the position (see below).
The National Grid referencing system is based upon the division of Great Britain into 100km squares, each assigned a two-letter code, e.g., TQ, SS, NY, etc. References to positions within any square may be made by means of the eastings and northings in metres from the bottom left hand corner of the square.
For example, SS 78382 87596 refers to a point 78382 metres east and 87596 metres north of the bottom left of the SS square.
When using National Grid references, the reference you give not only specifies a position, but also the extent of the map to be displayed (the precision).
The number of digits in the easting and northing give the precision.
The position used in the example above (SS 78382 87596) could be approximated to the nearest kilometre as: SS 78 88.
Alternatively it could be specified to the nearest millimetre by adding three further digits: SS 78382452 87596584
SS 78 382 452 87 596 584
100km square km m mm km m mm
Precision of National Grid references:
| SS | zooms to show a 100km square |
| SS 7 8 | zooms to show a 10km square |
| SS 78 88 | zooms to show a 1km square |
| SS 784 876 | zooms to show a 100m square |
| SS 7838 8760 | zooms to show a 10m square |
| SS 78382 87596 | zooms to show a 1m square |
Click to return to www.cadcorp.com
© Copyright 2000-2017 Computer Aided Development Corporation Limited (Cadcorp).