
What is a Cadcorp Base Dataset (BDS)?
Constructing graphics on a BDS overlay
A Cadcorp Base Dataset (BDS) is a native geometry format within SIS, used for storing and sharing your own graphic information. It supports complex vector, topological geometry and raster images.
A BDS file may be placed anywhere on your computer or on a network, it may therefore be accessed by other users if required. It provides a permanent and separate storage facility for the data you put in it.
To create a BDS open the Overlay Types dialog and select the Create new file icon:

Navigate to the required folder, select Cadcorp Base Dataset (*.bds) from the Files of type drop-down box, enter a file name and click Finish.
To open an existing BDS file open the Overlay Types dialog and select the File icon:
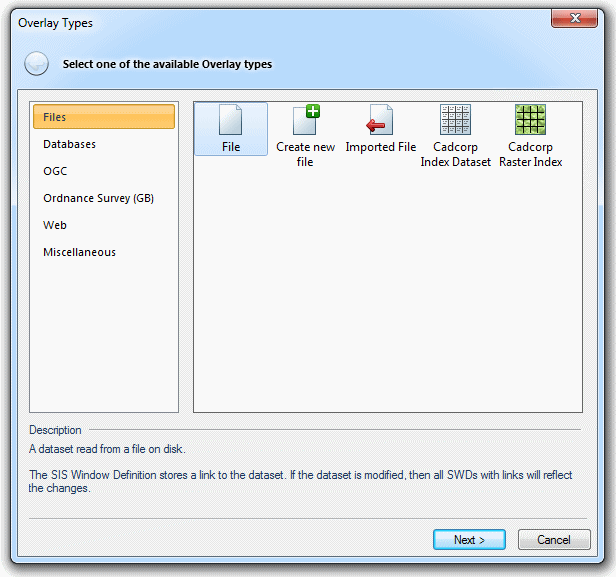
Click Next.
Navigate to the required folder, choose Cadcorp Base Dataset (*.bds) from the Files of type drop down box, select the required file and click Finish.
Display the Overlays dialog, either from Overlay [Home-Map] or by clicking F2.
Click the Dataset Properties... button on the Dataset tab of the Overlays dialog:
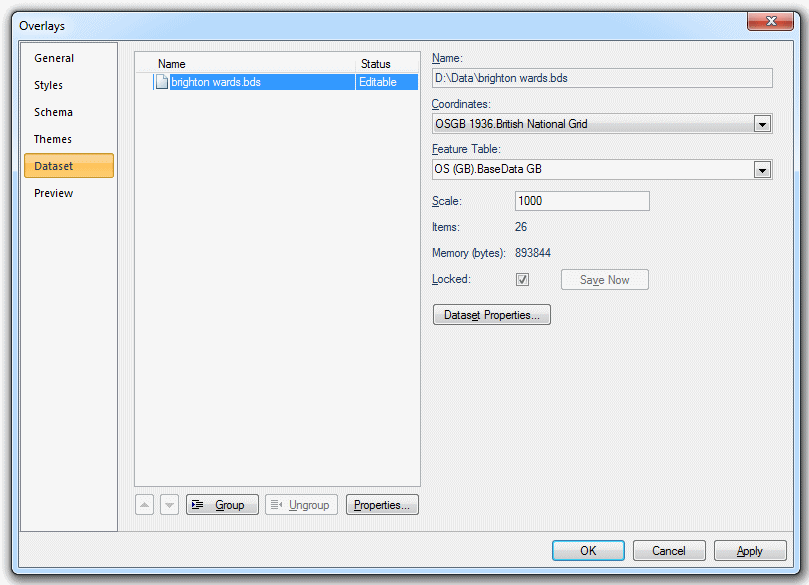
A dialog of the following form will be displayed:
.gif)
Coordinates
The coordinate system that the dataset items are defined in. To view or edit the coordinate system details drop down the combo-box list, and press the right arrow at the bottom.
Feature Table
The feature table to use for feature-coded items in this dataset. Feature-coded items get information about their feature code either from this feature table, or, if set, their own Feature Table property.
If applicable the Feature Table box will show the feature table to use for feature-coded items in this dataset. Feature-coded items get information about their feature code either from this feature table, or, if set, their own Feature Table property.
 FT drop-down.gif)
Scale
This is the default viewing scale for the dataset. This will affect how Text items convert their point heights into world sizes.
Items
The number of items in the dataset.
Memory (bytes)
The amount of memory that SIS is using to store the dataset. This number may be different from the size of the dataset file on disk.
Click the Properties... button to display the BdsDts dialog:

This dialog shows the properties of generic objects, (e.g. Dataset, Overlay).
To add a new attribute click the Add... button, the New Attribute dialog will be displayed:
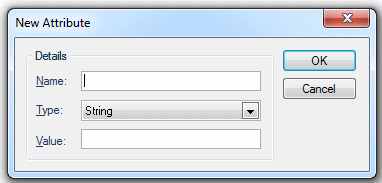
Enter details of the new attribute; Name, Type (select from drop-down box, see Attributes Overview) and Value.
Click OK.
The new attribute will be shown in the BdsDts dialog.
New attributes can be removed by selecting them in the BdsDts dialog and clicking the Remove button.
As you construct graphical items, they are placed on the current overlay. To make the BDS current use its local Make Current command in the Maps Control Bar or the Libraries Control Bar.
The BDS status must also be set to Editable (in the General tab of the Overlays dialog). For details of the image status options of editable, hittable, visible and invisible, see The Overlays dialog.
As soon as you create the BDS as described above, it exists in the location where you created it. However, the graphics you construct on this BDS are not saved until you either:
When you create a BDS, or are the first person to open an existing one, you are given ownership of it. The owner of a BDS is the only user who can edit it, although other users may have simultaneous read-only access.
If you are the owner of the overlay, unchecking the Locked tickbox on the Dataset page of the Overlays dialog allows you to disown it. If you are not the owner, checking this box allows you to become the owner, as long as no-one else owns it at the time.

If you choose to disown the file, you will be asked whether or not your changes should be saved first:
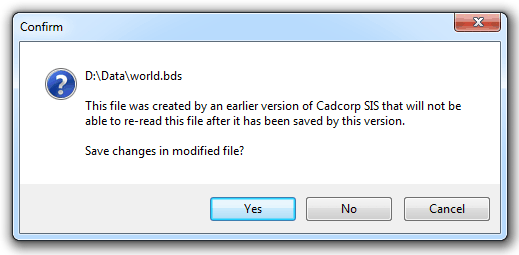
If the owner of a BDS relinquishes ownership, by unchecking the Locked tickbox, another user may then become the owner by checking the Locked tickbox on their own system. The new owner then gets editable access to the BDS.
Other users of the BDS
Other users may also call up the BDS into their Overlays dialog, but with a maximum status of Hittable. This means they can view it, but they cannot edit it.
The version of the BDS viewed by non-owners is always the most recent version saved to disk. Therefore, if relinquishing ownership, or before a non-owner can receive updates made in the current session, the owner must first save it.
If a non-owner of a BDS wishes to see the latest amendments made and saved by the owner in a current session, they should either:
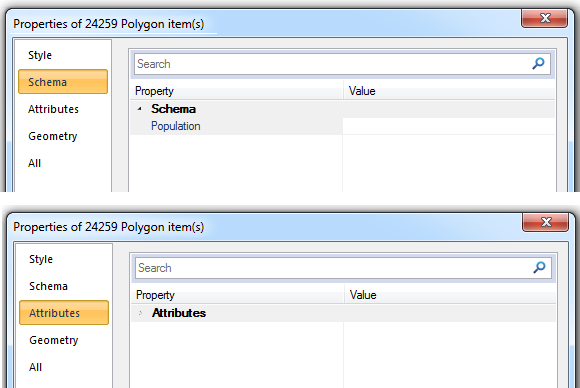
When you select all in a BDS overlay only Schema columns that have an entry in every single selected item will be shown in the Attributes tab of the Item Properties dialog.
Note: Due to the flexible nature of BDS files it is not necessary that all items have the same set of attributes. For example; Item A could have attribute of Name, Item B could have attribute Details, Item C could be a bitmap. This means removal of attributes can only occur when all items selected have those attributes.
For example if a BDS overlay contains Polygon Items and has a Schema column called Population, but not all the Polygons have a Population value, then selecting all the Items will result in the following where the Schema tab shows the Population property but the Attributes tab shows no Attributes:
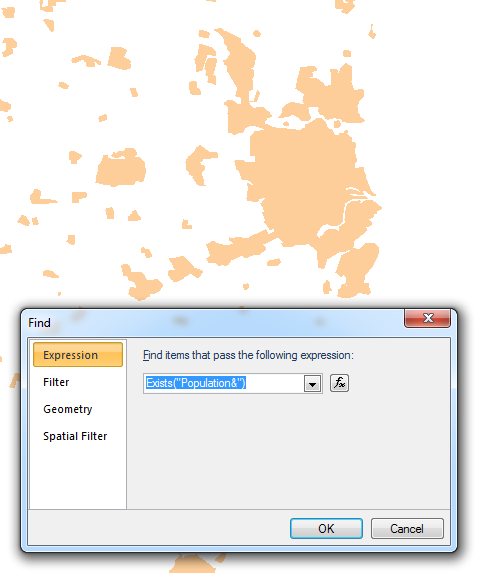
In order to find Items with the required Attribute select Find [Home-Selection] and use the Exists("AttributeName#") function. In this example this would be Exists("Population&").
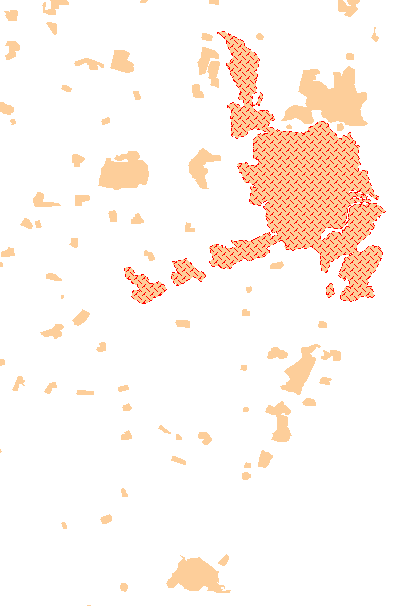
Items with an Attribute property value i.e. Population& will be shown selected:
Right-click and select Properties:
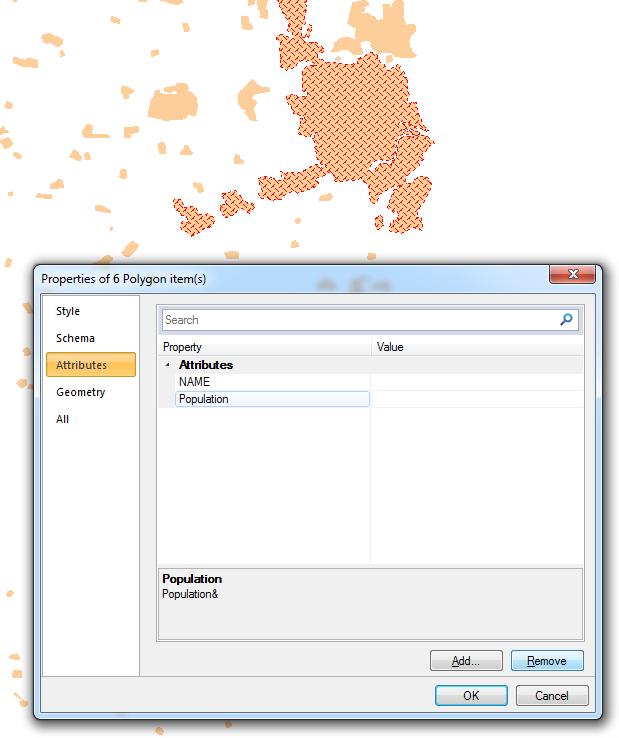
Highlight the Attribute and click Remove to remove it.
The Attribute will be permanently removed once you save the BDS.
BDS and FDB files are both standard Cadcorp formats. The choice of file formats depends on their use, the details of each file type are summarized in the following table.
| Base Dataset (BDS) | Feature Database (FDB) | |
| Geometry | Stores complex vector, topological geometry and raster images. | Well-known-binary format used for geometry, i.e. compatible with OpenGIS Simple Features Specification. No topology, no cartographic text (use Point item with text attribute and create a Label theme) and no true arcs, circles (faceted) or Beziers, i.e. supports only straight geometry. |
| Capacity | Limited | 1 Terabyte |
| Read as | Memory | Cursor |
| Considerations | Dates held formatted, (i.e. 12/6/2009)
Boolean held formatted, (i.e. True/False), but displayed in table window 0=True, 1=False |
Dates held in Julian format, (i.e. 41255).
Boolean held and displayed as 0=True, 1=False. |
| Advantages | Items can each have different attributes.
Item styles stored. Complex geometry stored. |
Items all have the same attributes.
Multi-user editable with feature level locking. |
| Disadvantages | Can be multi-user Hittable, not multi-user Editable | No storage of Item styles.
Simple geometry only stored. |
Send comments on this topic.
Click to return to www.cadcorp.com
© Copyright 2000-2017 Computer Aided Development Corporation Limited (Cadcorp).